The digital revolution has had a profound impact on the global economy, transforming the way we live, work, and do business. It has created new opportunities for innovation and growth, while also posing significant challenges in terms of job displacement, privacy, and security.
As the digital revolution continues to evolve, it is likely to bring about further changes to the global economy, shaping the future of work and driving economic growth and development in new and diverse ways. In this article, we shall discuss the digital revolution, timeline, and inventions that marked the period.
See also: The Industrial Revolution and its Consequences
What is the digital revolution?
The digital revolution also known as the third industrial revolution is a term used to describe the ongoing transformation of the global economy through the integration of digital technologies, automation, and advanced manufacturing techniques. It builds upon the previous two industrial revolutions and is characterized by a focus on automation, connectivity, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This ushered the beginning of the information age otherwise known as the digital age or computer age, which brought about the rapid development and widespread adoption of computer and communications technologies.
The third industrial revolution was marked by the emergence of new forms of information storage, processing, and communication, which have transformed virtually every aspect of modern life. The origins of the information age can be traced back to the invention of the computer in the mid-20th century. The first electronic computers were developed in the 1940s and 1950s and were primarily used for scientific and military purposes, such as code-breaking, weather forecasting, and nuclear weapons research.
In the 1960s and 1970s, computers began to be used in business and government, and the development of computer networks such as ARPANET (the precursor to the internet) paved the way for new forms of communication and information sharing.
The development of the microprocessor in the 1970s and 1980s made computers smaller, cheaper, and more accessible, leading to the proliferation of personal computers in the 1980s and 1990s. At the same time, other key technologies were emerging that would shape the information age.
For example, the development of fiber-optic cables in the 1970s and 1980s made it possible to transmit vast amounts of data over long distances, while the invention of the World Wide Web in 1989 made it easier for people to access and share information online.
The rise of the information age has had profound implications for virtually every aspect of modern life. It has transformed the way we communicate, work, learn, and entertain ourselves, and has created new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs to reach customers and markets around the world.
An important aspect of the digital revolution is the use of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, which allows for the creation of complex and customized products with greater speed and efficiency than traditional manufacturing methods.
This third industrial revolution is also characterized by the increased use of renewable energy and the transition to a more sustainable economy.
As companies seek to reduce their carbon footprint and become more environmentally friendly, there is a growing focus on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, and the development of smart grids and other technologies that can optimize energy usage and reduce waste.
See also: Factories in the industrial revolution
When did the digital revolution start?
The digital revolution began in the late 20th century, as advancements in technology and computing power made it possible to connect and automate industrial processes in new ways. The use of computer-controlled machines and robots allowed for greater precision and efficiency in manufacturing, while the development of the internet and other digital technologies enabled companies to communicate and share information in real-time, regardless of their location.
One of the key components of the digital revolution is the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to the interconnection of physical devices and everyday objects through the Internet. By embedding sensors and other data-gathering devices into machines, products, and even buildings, companies can collect and analyze vast amounts of data about their operations, allowing them to optimize processes and make more informed decisions.
See also: What came after the industrial revolution?
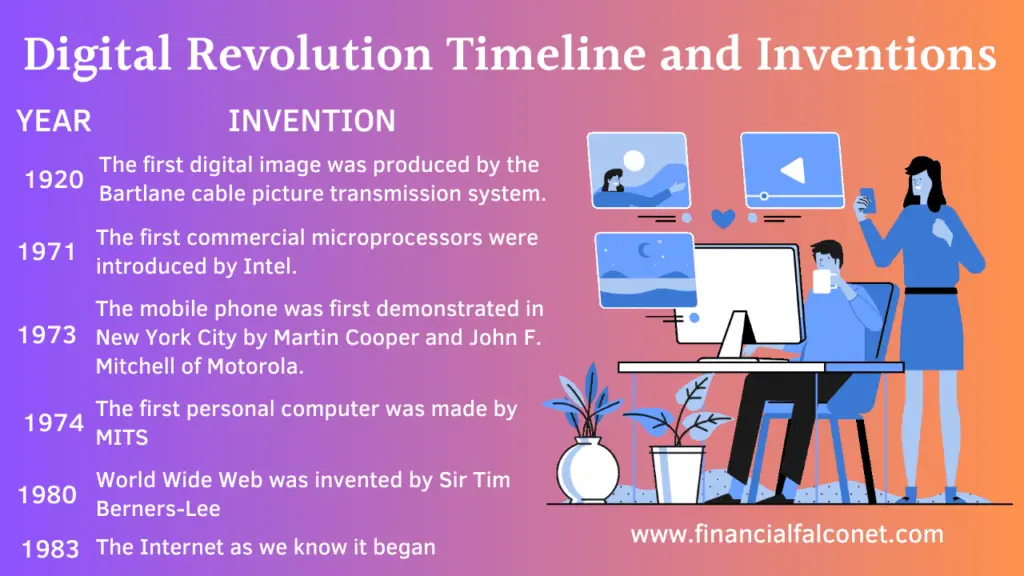
Digital revolution timeline
| Year | Digital revolution inventions |
|---|---|
| 1920 | The first digital image was produced in 1920 by the Bartlane cable picture transmission system. |
| 1971 | The first commercial microprocessors were introduced by Intel in 1971. It was known as the 4-bit Intel 4004 and was soon followed by the 8-bit microprocessor Intel 8008 in 1972. |
| 1973 | The mobile phone was first demonstrated in New York City on April 3, 1973, by Martin Cooper and John F. Mitchell of Motorola. This phone operated on the Bell Labs Advance Mobile Phone System (AMPS). |
| 1974 | The first personal computer was made in 1974 by Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS) company. This personal computer was named the Altair. |
| 1980 | World Wide Web was invented by Sir Tim Berners-Lee in the late 1980s. It is often simply called the web and is a system of interlinked hypertext documents that are accessed through the Internet. |
| 1980 | Wireless technology was first successfully used in 1895 when Guglielmo Marconi received Morse code on a radio wave transmitted by a spark-gap transmitter with a receiver 2.4 km away. This is the bedrock upon which wireless technologies such as TV, Radio, Bluetooth, and other wireless communication were predicated upon starting from the 1980s. |
| 1983 | The Internet as we know it began when the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) adopted the Transfer Control Protocol/Internetwork Protocol (TCP/IP) on January 1, 1983. |
| 1983 | Digital printing began when the Indigo and the Xeikon digital presses were launched at the IPEX trade show in Birmingham in the UK in 1983. The first digital print was released on watercolor paper in 1989. |
| 1969 | The first-ever commercial online service, CompuServe was launched in 1969 by two electrical engineering students from Columbus, Ohio. |
| 1982 | Boston Computer Exchange was the first online marketplace, it opened in 1982. |
What were the major inventions of the digital revolution?
The major inventions of the digital revolution include microchips, personal computers (PCs), the internet, World Wide Web, digital media technologies, E-commerce, and online marketplaces
See also: Political Effects of the Industrial Revolution
Inventions of the digital revolution
- Microprocessors
- Personal Computers (PCs)
- Internet and World Wide Web
- Digital electronics and automation
- Mobile and wireless technologies
- Digital imaging and printing
- E-commerce and online marketplaces
Above are some of the most significant inventions and innovations that were made in the digital revolution that transformed industries and paved the way for modern digitalization and automation. Let us discuss each one.
Microprocessors
Microprocessors are often considered one of the key inventions of the digital revolution. A microprocessor, also known as a microchip or CPU (Central Processing Unit), is a tiny semiconductor device that contains millions or billions of transistors and other electronic components. It functions as the brain of a computer or digital device, executing instructions and performing calculations to process data.
Before microprocessors, computers were large, expensive, and mostly limited to research institutions or large organizations. Microprocessors made it possible to integrate computing power into smaller, more affordable devices, such as personal computers, laptops, smartphones, and embedded systems.
Microprocessors brought a significant increase in processing power, allowing for faster and more complex computations. This enabled the development of advanced software applications, such as operating systems, databases, and multimedia applications, which transformed industries such as telecommunications, finance, and entertainment.
The flexibility and programmability of microchips allow for the execution of different types of software and applications which enabled the development of a wide range of software, from general-purpose applications to specialized software for specific industries or tasks. It also made it easier to upgrade or enhance the capabilities of a microprocessor-based system through software updates, without the need for hardware changes.
Additionally, microprocessors enabled the development of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and embedded systems that could control and automate various processes in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. This led to increased productivity, precision, and efficiency in industrial processes.
Through networking interfaces, microprocessors allowed computers and other digital devices to communicate and share data over local or global networks, leading to the development of the Internet of Things (IoT). This has transformed industries such as transportation, logistics, and smart homes.
Microchips are the foundation of modern computers, embedded systems, and digital devices, and they have transformed industries such as telecommunications, computing, and electronics. The invention and widespread adoption of microchips during the third industrial revolution revolutionized the field of computing and enabled the development of smaller, more powerful, and affordable computers.
Personal Computers (PCs)
The development of personal computers (PCs) in the 1970s and 1980s brought computing power directly to individuals and small businesses, transforming how people work, communicate, and access information.
PCs became widely available and affordable, leading to the democratization of computing and driving innovations in software, networking, and user interfaces. Hence, personal computers are viewed as good inventions of the third industrial revolution. A personal computer is a general-purpose computer designed for individual use, typically equipped with a microprocessor, memory, storage, and input/output devices, such as a keyboard and monitor.

The development of personal computers brought computing power to the masses, allowing individuals to own and use their own computers for various purposes, such as word processing, spreadsheets, graphics, and gaming. This democratization of computing empowered individuals and small businesses to perform tasks that were previously limited to large organizations or research institutions, leading to increased productivity and innovation.
With personal computers connected to the Internet, individuals gained access to vast amounts of information and the ability to communicate globally through email, web browsing, and social media. This transformed industries such as media, entertainment, and communication, and changed the way people communicate, access information, and consume content thus PCs facilitated easy access to information and communication.
Personal computers enabled digital creativity by providing tools for graphic design, video editing, music production, and other forms of creative expression. This has revolutionized industries such as art, design, advertising, and entertainment, allowing for new forms of digital art, media production, and creative collaborations. The availability of software applications for office productivity, project management, and automation tools has streamlined business processes, improved efficiency, enhanced productivity, and enabled remote work.
PCs have further become popular platforms for gaming, with a wide range of gaming software and hardware options available. This has led to the development of a multi-billion-dollar gaming industry, with e-sports, online gaming, and virtual reality experiences becoming mainstream.
Personal computers being part of the digital revolution inventions have transformed industries by democratizing computing, providing access to information and communication, enabling digital creativity, enhancing productivity and automation, and revolutionizing entertainment and gaming. The widespread adoption of PCs has fundamentally changed how we work, communicate, create, and entertain ourselves in the digital age.
Internet and World Wide Web
The invention of the Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW) in the 1960s and 1970s, and their commercialization in the 1990s, transformed global communication and information sharing, thus they are perhaps the most significant inventions of the digital revolution. Although the terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably, they refer to different concepts. The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers and computer networks that communicate with each other using a common set of protocols, known as the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). The Internet enables the transfer of data, information, and communication across the globe, connecting individuals, organizations, and devices in a decentralized and distributed manner.
The World Wide Web, on the other hand, is a system of interconnected hypertext documents accessed through the Internet. The web is built on top of the internet and uses the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for transferring hypertext documents, commonly referred to as web pages, which are linked together through hyperlinks.
The web allows users to access and share information, media, and services in a user-friendly and interactive manner. Through web browsers, users can access vast amounts of information from around the world with just a few clicks. This has transformed industries such as journalism, education, research, and content creation, enabling easy access to information and fostering knowledge sharing.
The Internet has revolutionized communication by enabling real-time communication and collaboration across the globe. Email, instant messaging, social media, and video conferencing are some of the tools that have transformed how people communicate, collaborate, and share information in personal and professional contexts. This has had a profound impact on industries such as telecommunications, media, and advertising.
The Internet and World Wide Web have revolutionized commerce and services. E-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, and digital payment systems have transformed industries such as retail, finance, and travel.
Online services, such as cloud computing, online banking, and software-as-a-service (SaaS), have changed how businesses operate and deliver services. They have also transformed the entertainment and media industries as streaming services for music, movies, and TV shows, online gaming, and social media have changed how people consume and interact with digital content. This has disrupted traditional media and entertainment industries, reshaping how content is created, distributed, and consumed.
The Internet and World Wide Web have further fostered innovation and entrepreneurship. The ease of access to information, tools, and resources on the web has enabled startups and entrepreneurs to develop and launch new products, services, and business models. This has led to the rise of digital startups, online marketplaces, and disruptive technologies that have transformed various industries.
Consequently, the impact of the Internet and the World Wide Web which are inventions of the digital revolution revolutionized industries such as telecommunications, media, commerce, and education, enabling instant communication, access to information, and online transactions on a global scale.
Digital electronics and automation
The third industrial revolution was characterized by the widespread adoption of digital electronics and automation technologies in various industries. These inventions revolutionized the way industries operate, leading to significant advancements in productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
Digital electronics refers to the use of digital signals and circuits in electronic systems, as opposed to analog electronics which uses continuous signals while automation is the use of technology to replace or augment human labor in the production or operation of goods and services.
In the context of the third industrial revolution, the invention and widespread adoption of digital electronics were pivotal in transforming industries. Digital electronics enabled the processing, storage, and transmission of information in a binary format (0s and 1s), which allowed for precise and reliable control of complex systems.
Digital electronic devices such as microprocessors, memory chips, and digital sensors enabled the automation of various industrial processes, leading to increased precision, speed, and reliability. Automation technologies such as industrial robots, computer numerical control (CNC) machines, and automated assembly lines replaced repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, leading to increased efficiency, precision, and scalability.
Automation also enabled the integration of data-driven decision-making and real-time monitoring into industrial processes, leading to optimized production and resource utilization. Together, digital electronics and automation technologies revolutionized industries during the third industrial revolution. They enabled the development of smart factories, where machines and systems communicate, analyze data, and make decisions autonomously, leading to highly efficient and flexible manufacturing processes.
These technologies also paved the way for the development of new business models, such as e-commerce, digital supply chains, and data-driven decision-making, which have transformed industries across the world.
The development of digital electronics and automation technologies, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotics, and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), revolutionized industrial processes and manufacturing.
Automation technologies enabled increased productivity, precision, and efficiency in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and logistics. Therefore, the third industrial revolution marked a significant leap forward in the use of digital technologies and automation in industries, leading to unprecedented advancements in productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
Mobile and wireless technologies

Mobile and wireless technologies are innovations that emerged as part of the broader digital revolution. The invention and widespread adoption of mobile and wireless technologies, such as mobile phones, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, revolutionized communication and enabled the development of mobile computing, e-commerce, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Mobile technologies, specifically referring to the development and widespread use of mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, have transformed the way people communicate and access information. Mobile devices have become ubiquitous, providing users with unprecedented levels of connectivity and access to information, entertainment, and services on the go.
Mobile technologies have enabled people to communicate and collaborate seamlessly across geographic boundaries, access the internet and social media, and use various applications and services for communication, entertainment, and productivity.
Mobile technologies have also facilitated the rise of mobile commerce (m-commerce), allowing users to shop, pay, and conduct financial transactions using mobile devices, leading to significant changes in the retail and financial sectors.
Wireless technologies, including wireless communication networks such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, have revolutionized the way people connect and communicate without the need for physical cables or wires.
Wireless technologies have enabled the proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing various devices and systems to communicate and share data wirelessly. This has led to the development of smart homes, smart cities, and smart industries, where devices and systems are interconnected, allowing for seamless communication and coordination.
Wireless technologies have also transformed industries such as logistics, transportation, and healthcare, enabling real-time tracking, remote monitoring, and data exchange, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
In summary, mobile and wireless technologies are major inventions of the digital revolution that have transformed the way people communicate, access information, and interact with technology. They have enabled unprecedented levels of connectivity, mobility, and access to information and services, leading to significant changes in various aspects of modern life and driving innovations across industries.
Digital imaging and printing
Digital imaging and printing are inventions that emerged as part of the third industrial revolution, these technologies revolutionized the field of imaging and printing, enabling digital capture, manipulation, and reproduction of images and documents, leading to significant advancements and changes in the way information is created, stored, and shared.
Digital imaging involves the capture, processing, and storage of images in digital format, as opposed to traditional film-based photography. The invention and widespread adoption of digital imaging technologies, such as digital cameras, scanners, and image editing software, during the third industrial revolution, transformed the field of photography and imaging.

Digital imaging enabled the capture of images in a digital format, allowing for instant preview, manipulation, and sharing of images. It also facilitated the development of new imaging techniques, such as digital radiography in healthcare, digital microscopy in research, and computer-aided design (CAD) in engineering and architecture.
Digital imaging has also revolutionized the entertainment industry, enabling digital special effects, virtual reality, and augmented reality experiences.
Digital printing is a printing method that involves the direct printing of digital files onto various substrates, such as paper, textiles, and plastics, without the need for traditional printing plates.
It has enabled high-quality, on-demand, and personalized printing, allowing for customized marketing materials, packaging, signage, and other printed products. It has also revolutionized the publishing industry, enabling print-on-demand services, digital publishing, and e-books. Digital printing has also been widely used in industrial applications, such as product labeling, packaging, and 3D printing.
The invention of digital imaging and printing technologies, such as digital cameras, inkjet printers, and laser printers, revolutionized the field of photography, printing, and media. These have enabled high-quality, fast, and cost-effective production of images and documents, transforming industries such as photography, advertising, publishing, and packaging. They have further increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customization in the production of images and printed materials.
In essence, digital imaging and printing have transformed the way images and documents are created, reproduced, and shared, leading to significant advancements and innovations across industries during the third industrial revolution.
E-commerce and online marketplaces

The development of e-commerce and online marketplaces in the 1990s and 2000s have revolutionized the way businesses and consumers engage in commerce, changing the landscape of retail and commerce globally. E-commerce or electronic commerce is the buying and selling of goods and services over the Internet.
Online marketplaces are platforms that connect buyers and sellers, enabling them to engage in transactions online. Online marketplaces are platforms that connect buyers and sellers, enabling them to engage in transactions online. Online marketplaces have become a major part of the digital economy, facilitating the exchange of goods and services between businesses and consumers.
E-commerce has transformed the way businesses and consumers engage in commercial activities, eliminating the need for physical brick-and-mortar stores and enabling online transactions. E-commerce has become a global phenomenon, with online marketplaces and platforms allowing businesses to sell products and services to customers around the world.
E-commerce has expanded the reach of businesses, allowing them to tap into new markets, and has provided consumers with unprecedented levels of convenience and access to a wide range of products and services. Examples of online marketplaces include e-commerce platforms such as Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, and Etsy, as well as service marketplaces such as Uber, Airbnb, and Upwork.
Online marketplaces provide businesses with a global reach, allowing them to showcase their products or services to a large customer base. They also provide consumers with convenience, choice, and competitive pricing, making it easy to compare and purchase products or services from different sellers.
The impact of e-commerce and online marketplaces has been far-reaching and transformative. They have disrupted traditional retail models and business practices, changing the way businesses operate and consumers shop. Some of the key impacts of e-commerce and online marketplaces include:
- Globalization of commerce: E-commerce and online marketplaces have enabled businesses to expand their reach beyond local markets, connecting them with customers around the world. This has facilitated cross-border trade and has allowed businesses to access new markets and customers, leading to increased international trade and economic growth.
- Convenience and accessibility: Shopping has been made more convenient and accessible for consumers through E-commerce and online marketplaces as consumers can shop online 24/7 from the comfort of their homes or on the go using mobile devices. This has changed consumer behavior and expectations, leading to increased demand for online shopping and digital services.
- Increased competition: E-commerce and online marketplaces have increased competition among businesses, as they provide consumers with easy access to multiple sellers and options for products or services. This has forced businesses to adapt and innovate to stay competitive, leading to changes in pricing, marketing, and customer experience.
- Disruption of traditional retail: Traditional retail models have been disrupted leading to the decline of some brick-and-mortar stores and the rise of online retail. This has had significant implications for the retail industry, with businesses needing to adapt to the changing landscape of consumer behavior and preferences. For instance, instead of having several physical stores, a business may now have just one warehouse while having a digital store where people can easily make purchases.
- New business models: E-commerce and online marketplaces have enabled new business models, such as dropshipping, subscription-based services, and platform-based businesses. These models have disrupted traditional supply chains and business practices, leading to new opportunities as well as challenges for businesses.
- Job creation and digital skills: E-commerce and online marketplaces have created new job opportunities in areas such as e-commerce management, digital marketing, logistics, and customer service. They have also increased the demand for digital skills, such as online marketing, data analysis, and website design, creating a need for a skilled workforce in the digital economy.
Ultimately, e-commerce and online marketplaces are major inventions of the digital revolution that have transformed the way businesses and consumers buy and sell products and services. They have enabled global access to products and services, streamlined supply chains, and transformed industries such as retail, logistics, and finance.
See also: Social Effects of the Industrial Revolution
Last Updated on November 2, 2023 by Nansel Nanzip BongdapBlessing's experience lies in business, finance, literature, and marketing. She enjoys writing or editing in these fields, reflecting her experiences and expertise in all the content that she writes.
