The disadvantages of the digital revolution include increased cyber threats and cybersecurity risks, information overload, misinformation, job displacement due to automation, and some others which we shall discuss hereafter. Over the past few decades, technology has transformed our world at an unprecedented pace, bringing about sweeping changes in how we live, work, and communicate.
The digital revolution began with the advent of the internet which connected people across the globe like never before and paved the way for the digitalization of information and communication. The proliferation of smartphones, social media, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has further accelerated digital transformation, reshaping industries, and redefining our interactions with the world.
Due to the digital revolution, data has become the new currency, and information is now readily available at our fingertips. It has transformed the way we access information, communicate with each other, shop, bank, work, and entertain ourselves. It has also disrupted traditional business models, creating new opportunities and challenges for companies, governments, and individuals alike.
It has also brought about unprecedented connectivity, allowing us to connect with people from all walks of life, share ideas, collaborate on a global scale, and access vast amounts of knowledge. It has democratized access to information and empowered individuals to become creators and consumers of content, leading to a shift in power dynamics and a redefinition of traditional institutions.
Read about: Impact of Digital Revolution on Society
Disadvantages of the digital revolution
- Digital divide
- Increased dependence on technology
- Privacy and security concerns
- Information overload and misinformation
- Social and mental health impacts
- Changes in the labor market
- Environmental impact
- Disruption of traditional industries
- Increased cyber threats and cybersecurity risks
While the digital revolution has brought about many positive changes and benefits which we have discussed earlier, it also has some demerits as listed above. We shall discuss these disadvantages of the digital revolution below:
Digital divide
One of the disadvantages of the digital revolution is the digital divide. This refers to the gap between those who have access to digital technologies and those who do not, resulting in disparities in terms of information, communication, and opportunities.
Access to digital technologies, such as internet access, computers, and smartphones, is not evenly distributed across populations, regions, or countries. This can result in marginalized communities, rural areas, or developing countries having limited or no access to the benefits of digital technology, leading to social and economic disadvantages.
The digital divide can exacerbate existing inequalities, as those who do not have access to digital technologies may face limitations in education, employment, healthcare, and civic participation. For example, lack of internet access can hinder access to online educational resources, job opportunities, and telehealth services, which can impact individuals’ ability to succeed in the digital age.
Moreover, the digital divide can contribute to a knowledge gap where those without access to digital technologies may lag behind in terms of information, digital literacy, and skills needed in the modern workforce. This can perpetuate disparities in income, employment opportunities, and social mobility, creating a cycle of disadvantage for certain groups or communities.
Additionally, the digital divide can also result in social exclusion, as those without access to digital technologies may be disconnected from online social networks, information sharing, and participation in the digital economy. This can further isolate individuals or communities and limit their ability to engage in civic activities, express their voices, and exercise their rights in the digital realm.
Bridging the digital divide is crucial to ensure that everyone has equal opportunities to participate in the digital revolution and access its benefits. This requires efforts to improve digital infrastructure, affordability of internet access, digital literacy programs, and inclusive policies to address disparities in access to digital technologies. It is essential to promote digital inclusion and bridge the digital divide to ensure that no one is left behind in the digital age.
Increased dependence on technology
Increased dependence on technology is one of the disadvantages of the digital revolution. As digital technology becomes more prevalent in various aspects of our lives, people are increasingly relying on it for communication, entertainment, information, and other activities.
This can lead to a reduction in physical activity as people spend more time sitting and engaging with screens, leading to potential health issues such as sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and other related health problems.
Additionally, increased reliance on digital technology can lead to decreased social interaction, as people may opt for online communication over face-to-face interactions. This can result in reduced social skills, difficulty in building and maintaining meaningful relationships, and increased feelings of social isolation and loneliness.
Moreover, excessive use of digital technology can result in a loss of basic skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication. Reliance on search engines for information, for example, may reduce the ability to critically evaluate and analyze information, leading to shallow understanding or misinformation.
This can have negative implications on education, decision-making, and overall cognitive abilities. It is important to recognize that while digital technology has undoubtedly brought about many positive changes, such as increased connectivity and convenience, excessive dependence on it can have negative consequences on physical health, social interaction, and cognitive skills.
It is therefore crucial to strike a balance and use digital technology mindfully to mitigate these potential disadvantages of the digital revolution.
Privacy and security concerns
Another disadvantage of the digital revolution is privacy and security concerns. The increasing reliance on digital technology has led to the collection, storage, and sharing of vast amounts of personal data online. This has raised serious concerns about privacy and security.
Cybersecurity threats, such as hacking, phishing, and malware attacks, are rampant in the digital world. These threats can result in data breaches, where sensitive personal information such as financial data, personal identification, and confidential records can be accessed, stolen, or misused. This can have severe consequences, including financial loss, identity theft, and reputational damage for individuals and organizations.
In addition, the widespread use of social media and online platforms has raised concerns about the invasion of privacy. Personal information shared on social media, such as photos, locations, and preferences, can be collected and used for targeted advertising, surveillance, or other nefarious purposes without individuals’ consent. This erosion of privacy can result in a loss of control over personal information, leading to potential misuse or abuse.
Overall, privacy and security concerns in the digital revolution pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and society at large. It is crucial to implement robust cybersecurity measures, protect personal data, and promote digital literacy and critical thinking skills to navigate the complexities of the digital world and mitigate the potential disadvantages associated with privacy and security breaches.
Information overload and misinformation
The digital revolution has resulted in an overwhelming amount of information available online which can be overwhelming and challenging to navigate.
The abundance of information can lead to information overload, making it difficult for individuals to discern accurate and reliable information from misinformation, fake news, and propaganda. Sorting through the vast amounts of information available to determine accuracy and reliability can be challenging, leading to the spread of misinformation, fake news, and conspiracy theories.
This can have detrimental effects on decision-making, critical thinking, and public discourse which may result in undermining trust in institutions, eroding democratic processes, and spreading misinformation about health and safety.
With the ease of spreading information online, false or misleading information can spread quickly and widely, leading to confusion, polarization, and social unrest. This disadvantage of the digital revolution gets further exacerbated during crucial times such as during a pandemic or elections when people are in dire need of useful information and may hence fall prey to misinformation.
Social and mental health impacts
Another disadvantage of the digital revolution is the potential for increased social isolation and decreased face-to-face interactions. The pervasive use of digital technologies, such as social media, online communication platforms, and video streaming services, can lead to decreased human interactions and social connections.
While digital technologies have made it easier to connect with others online, they can also contribute to social isolation and loneliness. Spending excessive amounts of time online or engaging in virtual interactions may reduce opportunities for face-to-face social interactions, which are crucial for human well-being and social cohesion. This can lead to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and even depression, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly or those with limited social networks.
The increasing use of digital technology has raised concerns about digital addiction and its impact on mental health. Excessive use of social media, online gaming, and other digital platforms can lead to addiction, social isolation, sleep disturbances, and mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and cyberbullying.
Moreover, the digital revolution has changed the dynamics of relationships and interactions, as online interactions can lack the nuances and depth of face-to-face interactions. Online communication can be impersonal, leading to misinterpretations, misunderstandings, and conflicts.
Social media, in particular, can create a distorted sense of reality, where individuals may feel pressured to portray an idealized version of themselves or compare themselves with others, leading to feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem, and social anxiety.
Additionally, the pervasive use of digital technologies can also lead to addiction and compulsive behaviors. The constant need to be connected, check notifications, or engage in online activities can lead to a loss of control over technology use, resulting in negative impacts on mental health, productivity, and relationships.
The constant presence of screens and the pressure to be constantly connected can also contribute to decreased physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle.
To mitigate these potential negative social and mental health impacts of the digital revolution, it is important to strike a balance between online and offline interactions, prioritize face-to-face social connections, and practice healthy digital habits.
This includes setting boundaries for technology use, cultivating meaningful relationships offline, and promoting digital literacy and responsible use of digital technologies, especially among vulnerable populations.
It’s important to be aware of the potential social isolation and negative impacts of excessive technology use and take proactive steps to maintain healthy social connections in the digital age while protecting individual mental health.
Changes in the labor market
The digital revolution has led to automation and the use of artificial intelligence in many industries, which has the potential to displace jobs and disrupt traditional employment patterns.
This is another disadvantage of the digital revolution as automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have the potential to replace jobs that involve routine tasks such as manufacturing, data entry, and customer service, leading to job displacement for workers in those fields.
As digital technologies continue to advance, there is a growing concern that many jobs across various sectors may be at risk of automation, resulting in unemployment or underemployment for workers who are not equipped with the necessary skills for the digital era.
The digital revolution has also given rise to the gig economy, where temporary, contract-based, or freelance work has become more prevalent. While this offers flexibility and opportunities for remote work, it can also result in job insecurity, lack of benefits, and reduced labor protections.
Workers in the gig economy often lack job security, stability, and access to traditional employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Additionally, there is a growing concern about the widening economic inequality brought about by the digital revolution.
Access to digital technologies, such as high-speed internet and advanced computing devices, may not be evenly distributed across all communities, resulting in a digital divide that can exacerbate existing economic disparities. Individuals who lack access to digital technologies or digital literacy skills may face barriers to accessing job opportunities resulting in further inequality.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological advancements can also require constant reskilling and upskilling to remain employable in the digital economy. Workers who are unable to keep up with the evolving demands of the digital job market may face challenges in finding meaningful employment and may be left behind in terms of economic opportunities.
To address the potential job displacement and economic inequality associated with the digital revolution, it is important to invest in education and training programs that equip workers with the necessary digital skills for the future job market.
Policies and regulations that protect the rights and well-being of gig economy workers, such as fair labor standards and access to benefits, are also crucial. Bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to digital technologies and opportunities is essential to prevent further economic disparities.
Additionally, fostering a culture of lifelong learning and supporting ongoing skill development can help workers adapt to the changing demands of the digital economy and mitigate the negative impacts on employment and economic inequality.
Environmental impact
One of the most devastating disadvantages of the digital revolution is its impact on the environment. While digital technologies have brought about many positive changes, they also have negative environmental implications that are often overlooked.
One significant environmental concern associated with the digital revolution is electronic waste or e-waste. As technology rapidly evolves, devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets become obsolete quickly, leading to a high turnover rate of electronic devices. This results in a significant amount of electronic waste being generated, which contains hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium that can be harmful to the environment and human health if not properly managed.
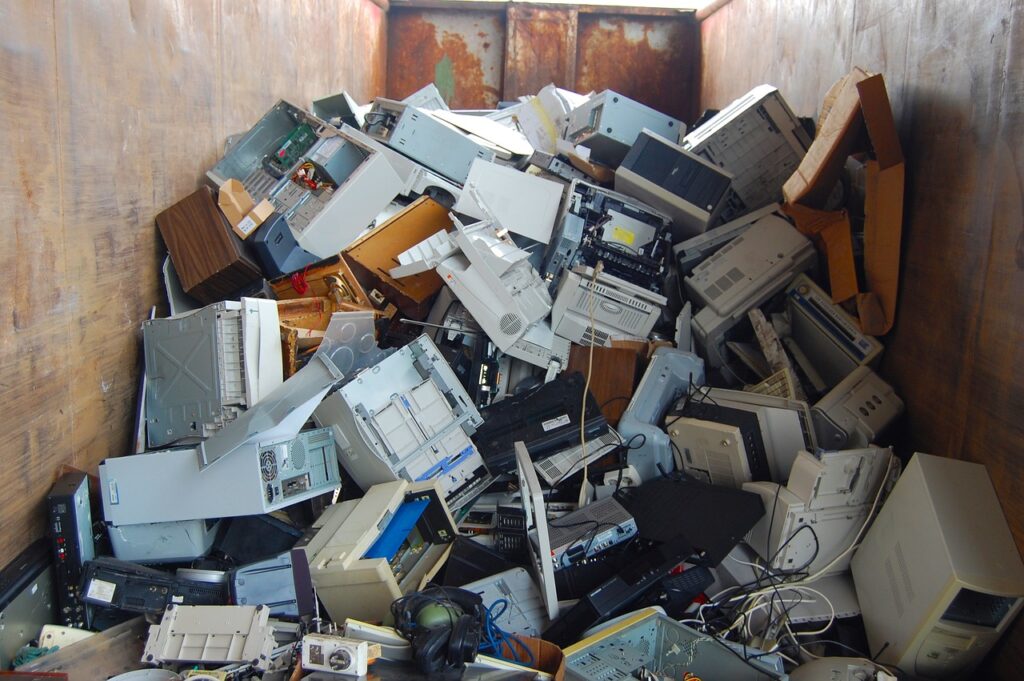

The improper disposal and recycling of e-waste can result in environmental pollution, soil and water contamination, and health risks for workers and communities involved in e-waste handling and disposal. E-waste is often shipped to developing countries with lax regulations for recycling and disposal, leading to environmental and health problems in those areas.
Moreover, the increasing demand for digital services and data storage requires massive data centers and cloud computing infrastructure, which consume large amounts of energy for their operation and cooling. This contributes to the carbon footprint of the digital revolution, as energy generation often relies on fossil fuels, leading to greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to climate change.
Furthermore, the constant need for upgrades and replacements of digital devices contributes to a throwaway culture, where devices are discarded rather than repaired or recycled, leading to unnecessary waste and resource depletion.
This results in a significant environmental impact associated with the manufacturing, use, and disposal of digital devices. To address these environmental challenges, it is essential to promote responsible consumption, proper recycling and disposal of electronic devices, and the adoption of more sustainable practices in the design, production, and use of digital technologies.
This includes promoting circular economy principles, extending the lifespan of digital devices through repair and reuse, and transitioning to renewable energy sources for powering digital infrastructure.
Disruption of traditional industries
Another disadvantage of the digital revolution is the disruption of traditional industries, such as print media and physical stores. The rapid pace of technological change can create challenges for individuals and businesses in adapting to new technologies and business models, leading to economic and social dislocation for those affected.
Digital technologies have enabled direct communication and transactions between consumers and producers, eliminating the need for intermediaries in many industries.
For example, online marketplaces such as Amazon have disrupted traditional retail supply chains by allowing consumers to buy directly from producers or manufacturers. This has impacted traditional distribution channels, wholesalers, and retailers, leading to changes in business models and supply chain strategies.
The digital revolution has enabled the emergence of new business models that disrupt traditional industries. For example, the sharing economy model, where consumers can share resources or services through online platforms, has disrupted traditional industries such as transportation (e.g., Uber and Lyft) and accommodation (e.g., Airbnb).
Crowdfunding platforms have also disrupted traditional financing models, allowing entrepreneurs to raise funds directly from consumers, bypassing traditional funding sources like banks.
Digital technologies have accelerated globalization, enabling companies to reach a global audience and operate across borders with ease. This has disrupted traditional industries by creating new opportunities for international competition and changing market dynamics.
For example, e-commerce platforms have made it possible for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to access global markets, challenging established players and disrupting traditional trade patterns. Print newspapers and magazines are also been gradually phased out as people prefer online news platforms and magazines to keep up with the latest happenings and trends.
Employees also tend to look for jobs that offer the opportunity for remote work, this has led to the closure of a lot of physical office branches and highly influenced official setups. Companies that have not adequately adjusted to this changing tide brought about by the digital revolution have found themselves tilting towards bankruptcy or being completely out of business.
Increased cyber threats and cybersecurity risks
Another disadvantage of the digital revolution is the potential for increased cyber threats and cybersecurity risks. As the reliance on digital technologies has grown, so has the vulnerability to cyber attacks, data breaches, and other malicious activities conducted online.
With the increased digitization of personal, financial, and sensitive information, there is a higher risk of cyber threats such as hacking, phishing, identity theft, and malware attacks. Cybercriminals continuously develop sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems, steal data, disrupt services, and cause financial and reputational damage to individuals, businesses, and even governments.
Furthermore, the interconnected nature of digital technologies means that a single vulnerability in one system can potentially have far-reaching consequences, leading to widespread disruptions, data leaks, and even societal impacts. For example, cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, or healthcare networks, can have severe consequences on public safety, economic stability, and societal well-being.
In addition, the rapid pace of technological advancements and the increasing complexity of digital systems pose challenges in keeping up with cybersecurity measures. Many individuals and organizations may lack the necessary knowledge, skills, and resources to effectively protect against cyber threats, leading to vulnerabilities and potential breaches.
The impact of cybersecurity risks goes beyond financial losses, as data breaches can also result in the exposure of personal information, leading to privacy concerns, identity theft, and loss of trust. Moreover, cybersecurity threats can also have psychological impacts, such as anxiety, stress, and fear, as individuals and organizations grapple with the potential consequences of cyber attacks.
To address the cybersecurity risks associated with the digital revolution, it is crucial to prioritize cybersecurity measures, such as regularly updating software and systems, implementing strong authentication methods, training users on safe online practices, and establishing robust incident response plans.
Collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals is also critical in addressing this particular disadvantage of the digital revolution as it requires a multi-faceted approach involving technical, policy, and human aspects to protect against cyber attacks and safeguard digital systems and information.
Read about: Digital Revolution Timeline and Inventions
What are the negatives of digital revolution?
The negatives of the digital revolution include the digital divide, disruption of traditional industries, increased dependence on technology, job displacement due to automation, privacy concerns, information overload, misinformation, increased cyber threats, cybersecurity risks, and social, environmental, and mental health impacts.
Even though these disadvantages of the digital revolution have far-reaching effects on individuals, businesses, and society, the digital revolution has also brought unprecedented benefits such as connectivity, access to information, and opportunities for innovation which have fundamentally transformed our world, reshaping our societies, economies, and cultures in profound ways.
As we continue to embrace the digital revolution, the challenges it poses require thoughtful consideration and action. It is essential to strive for inclusivity, ethics, and responsible use of technology to harness its full potential for the betterment of society.
Last Updated on November 2, 2023 by Nansel Nanzip BongdapBlessing's experience lies in business, finance, literature, and marketing. She enjoys writing or editing in these fields, reflecting her experiences and expertise in all the content that she writes.
