What is frictional unemployment?
Frictional unemployment is the type of unemployment that results when people voluntarily leave one job to search for another within the economy. It has to do with employment transitions. In other words, frictional unemployment occurs when workers choose to leave their jobs to search for new ones. Hence, the primary cause of frictional unemployment is workers leaving their jobs in search of another.
The workers that remain in their jobs until they find a new one are not part of the frictionally unemployed because they are never unemployed. Even in a stable growing economy, frictional unemployment naturally occurs. In other words, it is always present in the economy. Some frictional unemployment is inevitable because there will always be people transitioning from one job to another.
Frictional unemployment can be the consequence of people joining the workforce newly. It is a contributing factor to the overall unemployment as well as part of the natural unemployment which is the minimum rate of unemployment in an economy that results from economic forces and movement of labor. Natural unemployment is also a reflection of the number of workers who are involuntarily unemployed as a result of either skill inadequacy or replacement by technology.
Frictional unemployment definition in economics
The term frictional unemployment refers to persons who are out of work voluntarily while in search of another job. The frictional unemployment definition in economics explains that many people lose their jobs or resign and are in the process of searching for another one. This is job transitioning. Also, frictional unemployment is the result of workers entering the workforce for the first time.
The amount of frictional unemployment depends on the willingness of people to move to new areas to find jobs or move from one job to another. As we have seen, frictional unemployment arises when there is a transition from one job to another. An increase in frictional unemployment will signify that more people are leaving one job for another. Therefore, frictional unemployment is thought to explain relatively the inevitability of people leaving one job to search for another.
Oftentimes, economists make use of the term, frictional unemployment to make reference to both voluntary and involuntary unemployment. It is a component of the natural labor turnover rate and it is not a sign that the economy is unhealthy. An increase in frictional unemployment will depend on the increase in the number of people who transition from one job to another. However, frictional unemployment might be reduced if fewer people leave their jobs to search for another.
The role of unemployment insurance in frictional unemployment
Unemployment insurance increases the amount of frictional unemployment by bringing about a decrease in the opportunity cost of unemployment. In essence, this allows workers to be selective in the course of finding their next job which further adds to their time unemployed. This also means that binding minimum wages cause frictional unemployment. Nevertheless, many economists would argue that frictional unemployment is a normal phenomenon in an economy.
Usually, frictional unemployment goes up when the demand for labor is inadequate. As earlier stated, frictional unemployment will always exist since people will always leave their jobs to search for others. This means that frictional unemployment is present in an economy because of the transition from one job to another. Therefore, the gap that exists between the time a worker leaves his former job and the time he gets a new one indicates frictional unemployment.
Characteristics of frictional unemployment
- Voluntary
- Brief
- Natural
Frictional unemployment is usually voluntary, but it can be involuntary when the worker gets fired from his job and is in the process of searching for another. However, economists believe that frictional unemployment is less problematic than other types of unemployment because it is a reflection of the time it takes for workers to find jobs that best suit them. When workers move into jobs where they are most productive, it is a function of a healthy economy. Let’s look at the basic characteristics of this type of unemployment.
Voluntary
Unlike structural and cyclical unemployment, frictional unemployment is typically voluntary. This is because in this case, individuals choose to leave their jobs with the hope that they will find another one at roughly the same wage and skill level at a later time. In other words, they quit their jobs in search of better ones. While some workers do find better jobs, others have to settle for what they already had. In most cases, it is not the employers that ask the workers to leave.
Brief
Another characteristic of frictional unemployment is that it is temporary. It is in existence when one is transitioning from one job to another. Once an individual quits a job, it takes some time for them to find another job at comparable pay and level of qualification. During this brief period, frictional unemployment arises.
Natural
Frictional unemployment is oftentimes present in a healthy economy where the market encourages individuals to look for work that matches their set of skills and preferences. This is a result of the fact that individuals can confidently quit their current jobs to find a position that better suits them in a strong economy. Though a period will exist in which the person is not employed, we can assume that there is another job at comparable pay available to them. Therefore, frictional unemployment is a natural part of a market economy.
Causes of frictional unemployment
- An imbalance between workers and the jobs available
- Skill gap
- Dissatisfaction with work conditions
- Personal reasons
- Education
- Economic conditions
- Relocation
- Unemployment benefits
An imbalance between workers and the jobs available
Frictional unemployment is caused by an imbalance between workers and the jobs available. In general terms, workers follow a progression of careers throughout their working life, and as they advance in age, they move into more senior roles. However, frictional unemployment is likely to increase if there is greater pressure on the roles that are more coveted because individuals will wait to find something that suits them.
There are times when job seekers enter into new employment and think they are a good match and the job is what they desired. As time goes on and they become more accustomed to the role, it may not be their expectation or it may not be the type of position they desire in the long term. Because of this, they may leave their current role to join a field and industry that is completely different. This is usually common among students entering the market as at a young age, most of them do not know what they desire to do. Here, some experimenting may be necessary. This brings about frictional unemployment between jobs.
Skill gap
Frictional unemployment can be the consequence of the skill gap. This happens when employees prefer leaving when they find themselves incompetent for a job. In this case, it is concluded that they lack complete knowledge, skills, or expertise to fulfill their tasks.
Dissatisfaction with work conditions
Frictional unemployment comes about because of the fact that employees are not happy with salary levels, job responsibilities, commuting time, etc. There will be more likely for them to quit their jobs before having the chance to find another job.
Personal reasons
Workers can resign due to personal reasons and look for a new job to get back into the workforce. The reasons for quitting may be the need to move to another location, further studies, health conditions, raising a newborn child, an employee moving to be close to the job of his or her partner, etc.
Education
This occurs when a fresh graduate who has never been employed is unemployed until he joins his first job. In the period of waiting, such a graduate is frictionally unemployed.
Economic conditions
When an economy is booming and supportive, employment insurance has more room to support the unemployed until there is a replacement. Also with this, workers will have the courage to quit their existing job with the assurance that they will find a better one.
Information mismatch
This results when people are not aware of available job positions. Because they are not aware, they will be less likely to learn more about these positions. This calls for the availability of information with regard to open jobs.
Relocation
Frictional unemployment may arise as a result of one moving to a nicer city for certain reasons such as moving to live closer to a partner. Such decisions may also imply new jobs.
Unemployment benefits
Unemployment benefits as well as other forms of social security provide a safety net for people. This is a contributing factor to frictional unemployment because it gives job seekers more time and opportunity to be selective. Instead of going for the first job available to them, they will choose to look for more appropriate jobs. While this can be a contributing factor to frictional unemployment in the short term, it may reduce in the long term. It takes a long time for people to find the right job, then theoretically, there is a tendency for them to stay in that role for a longer period of time. This as well implies fewer changes in jobs thereby reducing the level of frictional unemployment.
Frictional unemployment examples
- Re-entrants after a career break
- Transitioning
- Job resignees
- New entrants into the workforce/fresh graduates
The examples of frictional unemployment are explained below;
Re-entrants after a career break
An example of frictional unemployment is when a nursing mother takes two years to break from her job for child care after having her baby. As the child is two years old, she is looking for a job again. Until this woman gets another job, she remains frictionally unemployed.
Transitioning
A worker is in a steady job as a software engineer. After some time, he then feels that he has developed adequate skill sets to hold the position of a software team leader. Because of this, he will begin to look out for another job. However, at the time he quits his job and is focusing basically on finding another one, he is technically unemployed at the moment.
Job resignees
A banking graduate went for a different job profile, that is, of operations executive but he always has a feeling of skill mismatch. Because of this, he decided to quit the job in order to find one in the finance field.
New entrants into the workforce/fresh graduates
A student who graduated from the university in the business field received a job offer as a supply chain manager in a leading company. However, her passion is in the subject of finance, and desires to make a career in that field. For a few months now, she has been looking for her dream job. The period in which she is unable to find her dream job signifies that she is technically unemployed. However, she is so confident that she will find a job within a short period of time.
Frictional unemployment Effects
Advantages
- Better positions of choice and job mobility
- Wider selection for businesses
- Posses less pressure on government resources
- Can be reduced quickly
- An indicator of a healthy economy
- Increases potential for higher productivity
- No downward pressure on wages
Better positions of choice and job mobility
Oftentimes, frictional unemployment is in existence in an economy that has a free-moving labor force and this is actually of great benefit because it is a sign that individuals are seeking better positions by choice. It is an indicator of job mobility, that is, individuals can transition between jobs with ease.
Wider selection for businesses
It is helpful to businesses because they have a wider selection of potentially highly qualified candidates that are applying for positions. This will help to reduce the level of unqualified employees in a firm.
Posses less pressure on government resources
Because it is short-term, there is not much drain placed on government resources.
Can be reduced quickly
Frictional unemployment can be reduced quickly because prospective job seekers can quickly be matched with job openings. The Internet has made this easier for individuals to find jobs that best suit them. Workers make use of social media and job posting websites to search for jobs, thereby, leading to quicker turnaround times in getting hired.
An indicator of a healthy economy
Because frictional unemployment shows that individuals are willing to forgo their current employment position with the confidence that they will find another job that better suits their preferences, it is an indicator of a healthy economy.
Increases potential for higher productivity
In the long run, frictional unemployment is a sign that individuals are finding the work that they desire. This in turn increases the potential for higher productivity. This will bring about an economy benefitting from individuals that are specialized in doing the work that tallies with their skillsets and preferences because they are likely to be more productive.
No downward pressure on wages
Frictional unemployment does not mean downward pressure on wages, unlike structural and cyclical unemployment where demand for labor is lagging behind the supply of demand. Theoretically, the market price of labor remains unchanged under frictional unemployment. This is because there is an assumption that another job is available for the individuals that choose to leave their jobs. The only thing that is lost here is the time it takes for one to transition from one job to another.
Disadvantages
Despite the advantages of frictional unemployment effects, there are disadvantages associated with it. If this form of unemployment goes beyond certain reasonable levels, it may have negative effects on the economy. It is for this reason that regulators will need to monitor levels of unemployment as well as take necessary actions to address the issue.
As earlier stated, frictional unemployment is natural in a healthy economy. This means that it does not always have a negative effect. In other words, it can be beneficial as we have seen above. However, one potential disadvantage of frictional unemployment is that employees may lose income even if it is only for a short period of time. This brings about challenges associated with managing personal and household expenses.
Moreso, even if this unemployment is temporary, it can be stressful for people and there is a risk of time of unemployment exceeding the expected time. The longer one is unemployed, there will be higher chances of experiencing some of the negative effects of unemployment.
Solutions to address frictional unemployment
- Make job information readily available
- Increase job flexibility
- Offer relocation assistance
- Resist discrimination against workers, jobs, or locations
- Reduce unemployment benefits
- Job and skill matching
- Investing in preparation
Government policies directed at reducing frictional unemployment include the enhancement of job flexibility among others which will be discussed below.
Make job information readily available
When individuals are not aware of available job positions, they are less likely to learn more about those positions. In order to increase the overall rate of employment, improving the availability of information related to open jobs is important. Employers can make this information available through different mediums including online job boards, social media platforms, and advertising campaigns. When the change of job information between employers and job seekers is faster, it will be quicker for people to find positions that meet their needs and qualifications.
Increase job flexibility
Job flexibility is usually attractive and this reduces the length of time of unemployment. Job flexibility can come in the form of offering flextime to allow employees to structure their workdays around their schedule or in accordance with their most optimal work times. Another way is to give employees the opportunity to work remotely as employees will be able to perform their jobs even if they do not live in the same location as the company. Employers can also incorporate part-time or half-day work options to allow employees to manage their commitments outside their respective jobs. There should also be development and training courses for employees to work on skills and potentially advance their positions.
Offer relocation assistance
This is a very good way of reducing frictional unemployment because it has a tendency of widening the pool of available job candidates. Offering relocation assistance can come in the form of giving relocation bonuses, reimbursing for moving expenses, and contributing to the living expenses of an employee until they are fully established in their new location.
Resist discrimination against workers, jobs, or locations
Regulators can place resistance to existing prejudice by increasing the attractiveness of certain workers, jobs, as well as locations. This will increase the ease of getting new jobs as well as employers getting qualified workers who will in turn increase productivity.
Reduce unemployment benefits
When the government lowers unemployment benefits, people will be encouraged to take a job quicker. However, there is no clarity with regard to whether this is desirable because it may encourage workers to take jobs that do not completely suit their skills.
Job and skill matching
When there is better matching of labor with vacant positions, workers will easily see the jobs that they should apply for. The unemployed can have quicker access to job vacancies through websites because therein, there is a comprehensive database for all positions. There is a case for the government to undertake comprehensive matching of jobs because private-sector competition may bring about diffusion in the market.
Investing in preparation
It will be helpful if applicants invest in job application preparation, especially for new entrants. They will be able to portray their skills accurately as well as ask the right questions in order to ensure that a potential job is a strong match. When there is a detailed and professional resume, cover letter, and polished interview, applicants will be able to communicate their job expectations and initiate a conversation with regard to whether the potential job is a strong fit or not. Time and skills are involved in writing cover letters and conducting interviews. Career services organizations can offer support as well.
How to calculate the frictional unemployment rate
It should be noted that the rate of frictional unemployment decreases during recessions. This is because employees are afraid of leaving their jobs because they lack other job options. This is the only type of unemployment that economic stimulus from the government does not affect. It does not come as a result of a shortage of jobs in the economy. In other words, it is not a symptom of the number of people in the labor force exceeding the number of jobs available in the economy. Frictional unemployment can result when there is an information mismatch.
Finding the frictional unemployment rate involves the number of workers searching for jobs and the total number of labor force/ Hence, we calculate the frictional unemployment rate by dividing the workers actively in search of jobs by the total labor force. The workers that are in search of jobs fall under three categories; workers who left their job, those that are returning to the workforce, and new entrants.
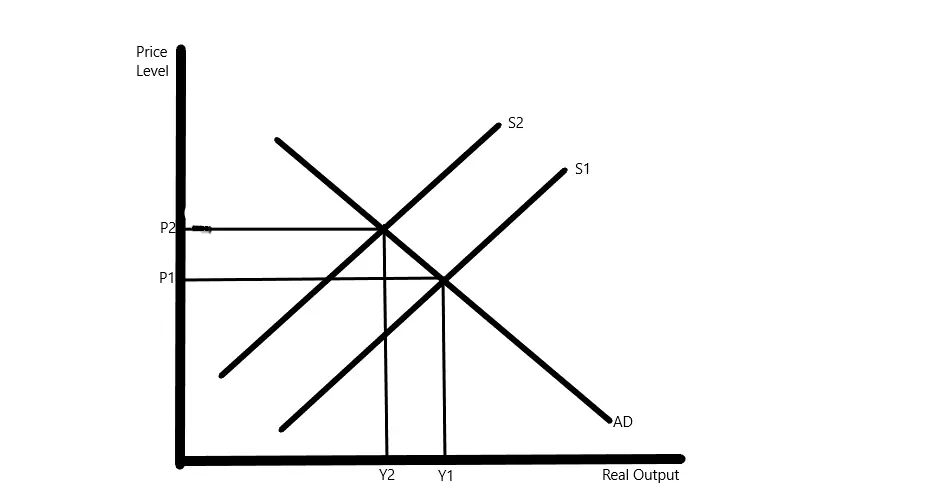
Frictional unemployment graph
In the graph below, workers make themselves unavailable for work thereby causing S1 to shift to S2 which results in unemployment. This lasts for only a short term as workers return to the state of employment thereby shifting from S2 to S1. Unemployment is therefore temporary as the long-run equilibrium Y1P1 is re-established.
Structural vs frictional unemployment
While structural unemployment results from the mismatch between the skills of the worker and the jobs available, frictional unemployment results when a worker is transitioning from one work to another. Structural unemployment is usually involuntary unlike frictional which is voluntary most times. Also, the duration of structural unemployment is usually longer than that of frictional unemployment.
Cyclical vs structural vs frictional unemployment
Cyclical, structural, and frictional unemployment are the major types of unemployment in an economy. However, they are different in their causes and nature.
Cyclical unemployment results when there is an economic downturn, while structural unemployment results when the skillsets of a worker do not match the jobs available. Frictional unemployment, on the other hand, results when a worker leaves his current job and is in search of another. While cyclical and structural unemployment are involuntary, frictional unemployment is usually voluntary. Frictional unemployment lasts for a shorter period of time compared to cyclical and structural unemployment. Structural cyclical and frictional unemployment may be interrelated but they are not caused by the same factors.
FAQs
What causes frictional unemployment?
The most common reason for frictional unemployment is workers leaving their current jobs to search for another one. Frictional unemployment is unemployment caused by factors such as skill gaps, dissatisfaction with working conditions, relocation, education, and unemployment benefits. Also, frictional unemployment can result when there is a poor allocation of workers.
What does frictional unemployment mean?
Frictional unemployment refers to the type of unemployment that results when people voluntarily leave one job to search for another within the economy. In other words, frictional unemployment results from the fact that individuals are transitioning from one job to another.
Is frictional unemployment included in the unemployment rate?
Yes, frictional unemployment is included in the unemployment rate.
Do binding minimum wages cause frictional unemployment?
Yes, binding minimum wages cause frictional unemployment.
Why is frictional unemployment of relatively little concern to economists or government officials?
This is because frictional unemployment tends to be a sign of a healthy economy in the sense that people confidently leave their jobs with the hope that they will find another of their preferences and skills. Also, it is a part of the market economy as there will always be people who will join the workforce newly as well as transition between jobs.
What is an example of frictional unemployment?
An example of frictional unemployment is a banking graduate who went for a different job profile, that is, of operations executive but he always has a feeling of skill mismatch. Because of this, he decided to quit the job in order to find one in the finance field. Frictional unemployment is most closely associated with job preference.
5+ years of professional experience in the business and finance sector with 1 year experience as a sales associate.
Writer, Editor, and economic activist.
