Nike’s supply chain management has been very good over the years and has helped the company to become the world’s largest seller of sports shoes and other sport wears. This doesn’t come easy because of the problems and challenges associated with managing the supply chain. We will analyze how Nike’s supply chain issues were managed to propel the company to success.
What is the Nike supply chain?
Nike’s supply chain process refers to all the steps involved in the production and delivery of the final Nike products to customers. The supply chain management starts with the procurement of raw materials, to logistics involved in transporting the raw materials to the factories, the conversion of the raw materials into finished products, and finally delivering it to the end customers.
Supply chain management is a complex process that a company must learn to overcome all the issues that may occur along the supply chain, in order to succeed.

See also: Starbuck’s Vertical Integration Strategy
Nike supply chain process
- Sourcing for raw materials
- Production
- Distribution of finished products to customers by the Nike supply chain team.
Sourcing raw materials
The first step in Nike’s supply chain process is sourcing raw materials. The company relies heavily upon independent contractors who source raw materials such as natural rubber, cotton, leather, EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate), etc, before delivery to the factories.
Production
The next step in the supply chain process of Nike is outsourcing the manufacturing to many independent factories in countries that meet its criteria.
The criteria are simple and include factories or manufacturers located in countries where the production is inexpensive with low import taxes and high levels of efficiency.
To maintain quality and standards, Nike places its officials to supervise the production process in these foreign factories.
Nike sustains this outsourcing strategy by continuously shopping for new manufacturing sites worldwide as far as the location can make the company more productive.
Distribution of finished products to customers by the Nike supply chain team.
Once the finished products are manufactured from the Tier 1 suppliers, Nike gets them over to the distribution centers who then deliver them to the multiple retail outlets they have.
Customers can then buy the final products from any of the retail outlets: these could be Nike’s branded stores, online stores, or any physical store available.
Related: Netflix’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Nike supply chain diagram
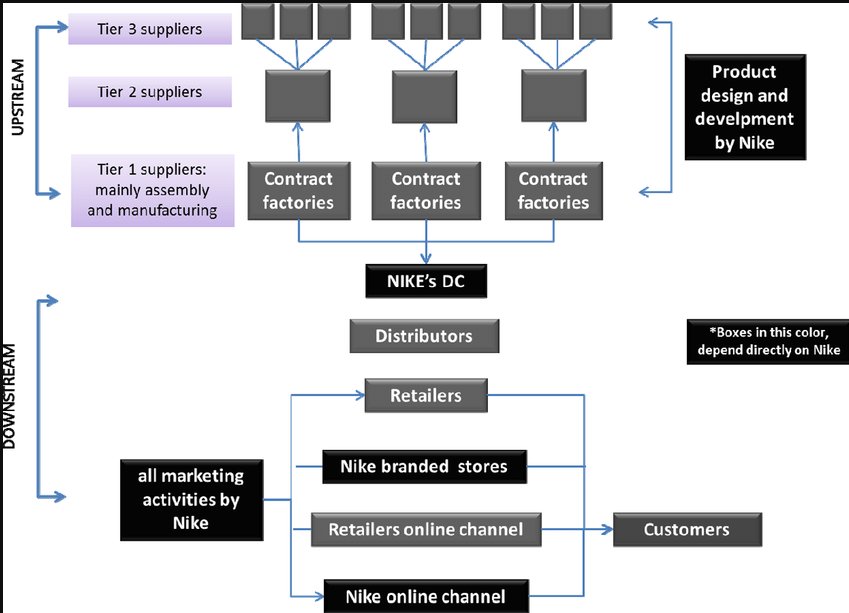
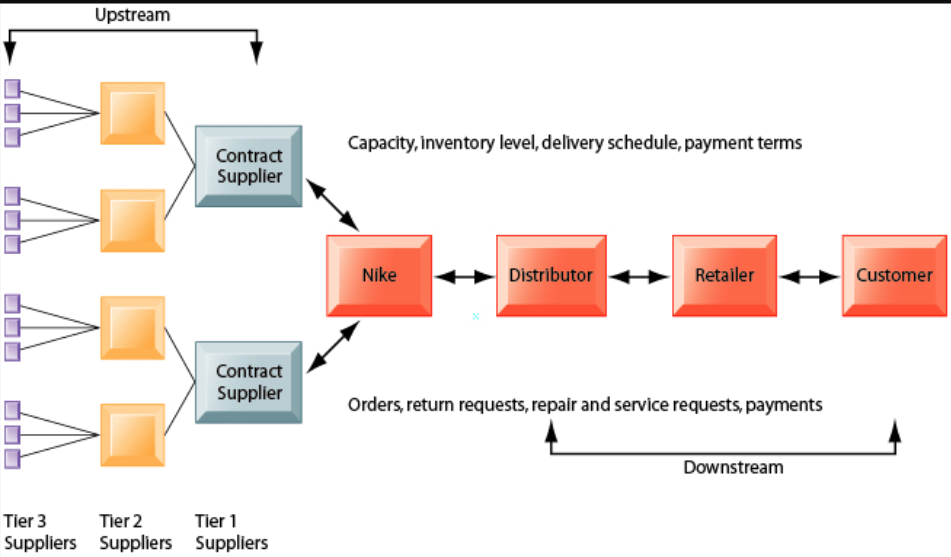
The Nike supply chain process can be divided into two major processes: the upstream and downstream processes.
The upstream processes of Nike’s supply chain include the raw materials suppliers, who can further be divided into tier 3, 2, and 1 suppliers.
The downstream part includes the distributors who are responsible for getting the finished products delivered to customers.
The Nike supply chain diagram is further simplified and explained below using the flow chart.
Nike supply chain flow chart
From the Nike supply chain diagram below, you can see how its supply chain works. It starts with sourcing raw materials from numerous suppliers and then transporting them to the factories for production, and finally the delivery of the final Nike products to consumers.
Tier 3 suppliers are the various farms where the raw materials are grown or harvested.
Tier 2 suppliers are factories that receive the raw materials from tier 3 suppliers and then process them into basic components that are needed for the manufacturing of the finished products.
The Tier 1 suppliers are the factories that receive different components from Tier 2 suppliers and couple these components into a single finished product. For example, tier 1 suppliers may need 3 different fabrics from 3 different tier 2 suppliers in order to sew a single Nike shirt as a finished product.
Once the final products are manufactured, Nike now transport them to the distribution centers.
The distributors now get it across to the various retail outlets where customers can directly buy these final products. The retail outlets can be Nike’s online shops, its branded physical stores, or any retail stores (whether online or physical that sell Nike’s products).
Nike’s supply chain flow chart can be simplified as:
Suppliers -> Manufacturer -> Distribution Centers -> Retail Shops -> Customers
Nike supply chain issues
- Excess Inventory
- Nike’s Supply Chain Ethical Issues and Human Rights Violations Scandals
- Economic and Industry Risks
- Transportation of major raw materials to factories
We will discuss each of these Nike supply chain issues below. The section that follows will discuss the details of Nike’s supply chain management and how the company resolves these stated issues.
Excess Inventory
One of Nike’s supply chain issues is excess inventory. This occurred in 2022 as a result of the effects of the 2019/2020 COVID pandemic. The pandemic caused global supply chain issues where both retailers and consumers were affected.
Why did Nike have inventory problems?
There were shipping delays and port congestion as a result of restrictions in many countries because of COVID-19. This resulted in retailers receiving inventory late or after the pandemic. After the pandemic, the rising inflation and recession made consumers change their buying habits. This means buying fewer products that are not necessities and more items that are necessities. This caused the accumulation of excess inventory for brands like Nike.
This Nike supply chain issue affected the profits and stocks of the company in the late 2022 and early 2023 fiscal quarters. The shares of the company dipped to their lowest price in more than two years following the announcement by the company of an increase in its inventories. The company said inventories rose 44% to $9.7 billion compared with the year-ago period.
Matthew Friend, Chief Financial Officer, of Nike Inc., says the company is taking steps to “take that inventory and more aggressively liquidate it so that we can put the newest and best inventory in front of the consumer in the right locations.”
Nike’s Supply Chain Ethical Issues and Human Rights Violations Scandals
One of the problems faced by Nike in its supply chain is accusations from activists about human rights violations in some of Nike’s factories.
In June 2019, Nike had the lowest rating from the Tailored Wages UK report because the company “can show no evidence of a Living Wage being paid to any workers“.
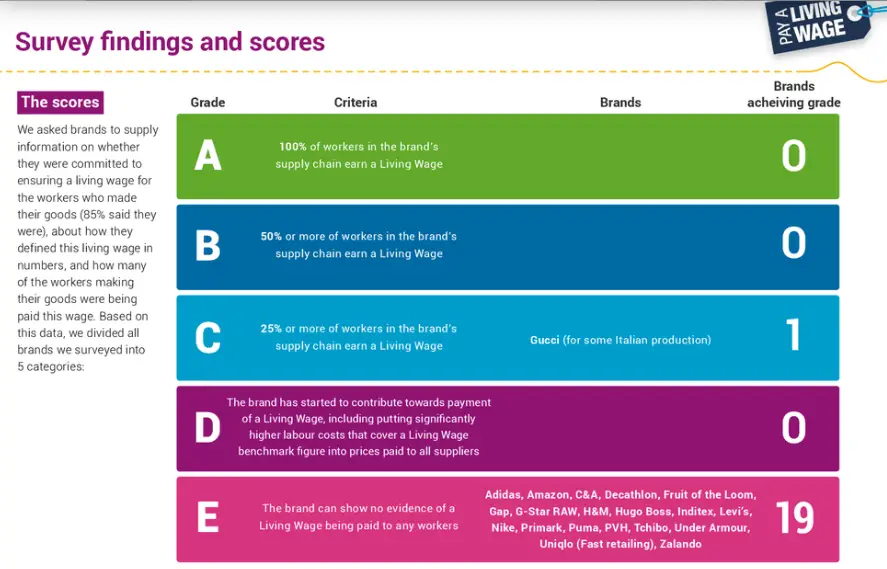
The report says:
“No major clothing brand is able to show that workers making their clothing in Asia, Africa, Central America or Eastern Europe are paid enough to escape the poverty trap“.
https://archive.cleanclothes.org/resources/publications/tailored-wages-2019-the-state-of-pay-in-the-global-garment-industry/view
Some Trade unions and workers’ rights NGOs have filed a case at the US National Contact Point for the OECD Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct at the US State Department.
They are accusing Nike of violating OECD guidelines; alleging that since the onset of Covid-19, garment workers in Nike’s supply chain have experienced arbitrary pay cuts, gender discrimination, layoffs, and unpaid wages for hours worked.
The group is demanding compensation for these Nike’s supply chain workers who are more than 450,000 in number, at 94 factories located in 5 countries.
In 2022, Tulipshare, an activist investor and shareholder advocacy group demanded that these garment workers should be paid fairly for making Nike clothes. The group wrote an open letter to Nike, questioning its unresponsiveness to these allegations of forced labor in its business operations.
They are asking Nike to embrace its corporate responsibility of respecting human rights by adopting the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights.– (PDF file)
Economic and Industry Risks
Economic problems, either globally or locally within the country in which a factory is located contribute to Nike’s supply chain issues. Because the company conducts transactions in different currencies, it is exposed to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates relative to the U.S. Dollar.
This means persistent volatility in the markets and exchange rates will negatively impact Nike’s supply chain process.
Also, trade restrictions in some countries have contributed significantly to the supply chain issues of Nike. For example, the company has made attempts to produce in Europe to make up for the high level of trade restrictions faced in China but has struggled to achieve the desired efficiency and productivity. The European manufacturers were never able to reach the efficiency of Asian factories because of Asia’s inexpensive labor.
Transportation of major raw materials to factories
Another issue of Nike’s supply chain is the problem of transporting raw materials to different factories across the world.
Natural rubber is the primary raw material for Nike’s shoes, and it is majorly cultivated in southeast Asia. This means when harvested from Asia, the raw materials must then be transported to factories located in other countries. Because of this dependence on Southeast Asia, any major disruption such as a natural disaster could cause serious shortages or even halt production of the affected Nike products in other countries.
See also: Companies with Vertical Integration Strategies
Other Nike supply chain issues
Nike’s supply chain issues mentioned and discussed above and not exhaustive; other problems still occur along the supply chain that are common in international trade.
Other Nike supply chain issues that are common in international trade
- Implementation of foreign and domestic trade policies
- Potential changes in foreign and domestic trade policies
- Increases in import duties
- Anti-dumping measures
- Limitations to revenue as a result of quotas
- Trade restrictions
- Restrictions on the transfer of funds
- Political instability in some countries
Nike supply chain management
Knowing how to manage the issues that arise from the supply chain process is what makes a company succeed more than its competitors. Nike’s supply chain management has been exceptional over the years because of its proactive approach toward resolving any supply chain issue that arises. These approaches toward resolving the problems that arise from its supply chain are listed and explained below.
How Nike manages its supply chain issues
- The use of many suppliers
- Outsourcing of manufacturing to many factories
- Building long-term relationships with efficient partners
- Proactive compliance with ethics and regulations
Let’s take a look at some of Nike’s supply chain strategies for resolving its common current and past supply chain issues.
The use of many suppliers
Nike uses numerous suppliers to overcome the supply chain problem of unpredictable occurrences such as accidents, disasters, extreme weather, etc.
When a company relies on a single supplier of raw materials, unwanted events may occur that could make the supplier unable to supply the raw materials at the needed time. A factory or farm could be razed down by fire, hurricanes or earthquakes may destroy the factory, etc.
When these occur, the supplier cannot meet the demand of the company and this presents a serious threat to the success of the company. It means there will be delays in production or in some cases, production may be halted pending when the company gets a new supplier.
This type of supply chain issue occurred in 2021 with Automobile manufacturers where a shortage of semiconductor chips forced some factories to halt production.
Tesla having vertically integrated most of its supply chain steps was not affected badly and was able to reconfigure its software to get around the chip shortage in time and continued production compared to its competitors who were forced to halt production.
Instead of vertical integration, this type of supply chain issue was resolved by Nike through the use of many suppliers. It means avoiding the reliance on a few suppliers but instead getting many suppliers to provide the same raw materials.
For example, Nike could contract several suppliers to provide natural rubber; the company will then ask other suppliers to provide leather, it will also outsource the supply of cotton to many other suppliers, and so on. This strategy means Nike will not rely on a single supplier to provide any raw component for its products.
To solve this Nike’s supply chain issue, the company outsources its manufacturing to more than 700 factories in 42 countries.
Nike also ensures that no supplier of raw should account for more than 5% of the total production output of any of these factories. That way, any unwanted event or problem affecting any facility cannot have any significant effect on production.
When manufactured, the products are then transported to 57 Nike distribution centers globally.
By using multiple suppliers for each type of raw material needed, Nike was able to solve the supply chain issue of unforeseen circumstances that could cause delay or halt production when a supplier is unable to meet demand. When one supplier is lacking, other suppliers can meet up with the supplies.
Outsourcing the manufacturing of products to many factories
Nike’s supply chain management also extends to the outsourcing of manufacturing to several factories in different countries of the world. These factories are not directly owned by Nike. The company outsources the manufacturing process as well.
The benefits of this strategy in Nike’s supply chain management are mainly to save time and money. The cost of building a factory in every new market or country that Nike would have wanted will be high. It means the company will have to buy land, build it, and start recruiting while also keeping to the rules and regulations required for setting up a company in various countries.
To avoid all these challenges while also saving time, reducing cost, and increasing efficiency, Nike decides to outsource its production to already established factories in any country of its choice. This means Nike will negotiate and sign a contract with established apparel and shoe manufacturers in a given country, then give them its guidelines and then train them on how to manufacture Nike’s products to meet quality and standards.
The outsourcing strategy also reduces the stress involved in registrations, licensing, and wait time required for approval in terms of ethics and government regulations across different countries.
Since the established factories have known the required regulations in each of their countries and locality, outsourcing to them also helps Nike to overcome this type of supply chain issue.
The last benefit of outsourcing production is to maintain quality and standards even with increased demand. Nike is an established and popular brand. In 2020, Nike manufactured more than 900 million finished products in order to meet the growing demand for its products.
When demand is high and a company tries to increase production using a single factory, there will be a compromise on quality and standards. In order to maintain quality, Nike outsources its manufacturing to more than 700 factories worldwide. This way, as the demand increases, Nike can increase supply without compromising on quality. All it needs to do is to get a new manufacturing partner to increase its products.
This Nike’s supply chain management helps it to quickly meet customers’ demand while staying ahead of the competition and maintaining its market share. Without this, quality will be reduced if the company were to try increasing output from a single facility; and when the demand is high, the company cannot meet up.
Building long-term relationships with efficient partners
Nike’s supply chain management has been successful in controlling some of the issues or challenges faced in its global supply chain by building and strengthening relationships with efficient manufacturers.
The company utilizes a small number of manufacturers who have the infrastructure and resources needed for the quality desired by Nike. Other things considered are technical know-how, labor management, and operational experience.
Nike, therefore, builds valuable relationships with these manufacturers, who may not necessarily ensure the lowest costs, but because of their efficiency and productivity. The benefits of this long-term relationship are shorter lead times for delivery, maintenance of standards and quality, and the ability to manufacture innovative products.
Proactive compliance with ethics and regulations
Ethical issues and regulations are some of Nike’s supply chain issues. The company manages these problems and challenges by taking proactive steps to ensure that all its suppliers and factories remain compliant and meet requirements and regulations.
Nike has shown the willingness to remain compliant with all regulations as seen in some of its partnerships. For example, in Turkey, Nike and other international brands joined a project created by the Fair Labor Association (FLA) and the İyi Pamuk Uygulamalari Derneği (IPUD) in order to improve employment practices in the Turkish cotton industry.
To further strengthen its commitment to remaining compliant with regulations and laws, Nike prioritizes suppliers and partners with demonstrable leadership in corporate responsibility. The company is also reducing the factories in its supply chain that inflict excessive overtime on their workers.
These strategies of Nike’s supply chain management have been beneficial to the company by making its products acceptable to society, increasing its profits and market share, and avoiding government sanctions.
Advantages of Nike’s Supply Chain Management
- Outsourcing of manufacturing helps Nike to quickly increase production when demand is high by simply partnering with more factories.
- When the demand is low or new markets are not favorable, because Nike does not own the factories, it becomes easier to leave an unfavorable market or country by simply ending its partnership with the factories.
- Outsourcing the supply of raw materials to numerous suppliers solves Nike’s supply chain issues of unfavorable and unforeseen circumstances that may affect any of the suppliers.
- Nike saves cost and time that would have been used for building new factories, by simply outsourcing it to already established factories in any region or country of choice.
Nike’s Suppliers
Who are Nike’s suppliers?
These are companies that supply raw materials to Nike’s factories. They are located in different countries and must meet certain requirements for Nike to work with them as its suppliers.
Where does Nike get its supply from?
Nike gets its supply from several countries of the world. For example, Nike gets the supply of cotton from the United State Of America, China, Turkey, and India. The company gets its leather from tanners and suppliers in China and Vietnam. Other raw materials such as natural rubber are supplied from Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia.
Nike supply chain map
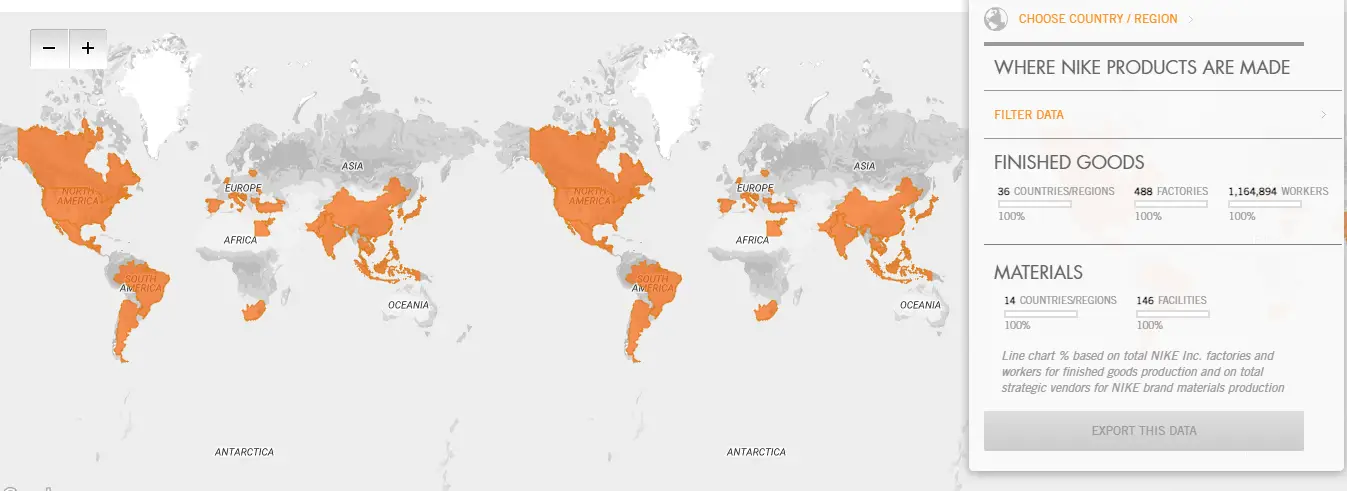
Source: Nike
A table showing the names and locations of Nike’s suppliers in the United States and the component that each company supplies.
| Names of Nike’s Suppliers | Raw material supplied | Location of suppliers |
|---|---|---|
| Pou Chen Corporation | Footwear | Taiwan, China, Indonesia, Vietnam |
| PT Pan Brothers | Apparel | Indonesia |
| Fulgent Sun Group | Footwear | Taiwan |
| Delta Galil Industries | Apparel | Israel, China, Indonesia |
| Eagle Nice International Holdings | Apparel | China, Vietnam |
Conclusion
Nike’s supply chain management has been crucial to its success as the world’s largest seller of sports shoes and sportswear. The supply chain process involves various steps, starting with sourcing raw materials, transporting them to factories, manufacturing the products, and finally delivering them to customers through distribution centers and retail outlets.
However, Nike has faced some supply chain challenges such as excess inventory which was an issue in 2022 due to shipping delays and changing consumer buying habits caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Other Nike supply chain problems include ethical concerns from human rights activists, economic and industry risks, and trade restrictions in some countries.
Despite Nike’s supply chain issues and problems, it has used its management strategies to overcome them and maintain its position as a leader in the sports apparel industry through multiple suppliers and outsourcing production.
Related:
- IKEA Supply Chain Problems and Issues
- McDonald’s Supply Chain Issues and Process
- Telstra’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Nansel is a serial entrepreneur and financial expert with 7+ years as a business analyst. He has a liking for marketing which he regards as an important part of business success.
He lives in Plateau State, Nigeria with his wife, Joyce, and daughter, Anael.
