So many consumer products companies today, are under tremendous profit margin pressure. As a result, companies like Starbucks Corporation resort to using vertical integration strategies in order to maximize profits and stay ahead of their competitors. Through Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy, the company has been able to offer handcrafted beverages, several blends of coffee, merchandise, and food items to customers at the best quality. Thus, making it superior to its competitors.
This well-known specialty coffee retailer uses both backward and forward vertical integration strategies to maximize profits. In this article, we will discuss Starbucks’ vertical integration strategies and how this business strategy has enabled the company to remain the world’s largest coffeehouse chain.
Related: Amazon’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Vertical integration meaning
Vertical integration is a type of business strategy wherein a company takes direct ownership of multiple stages of its supply chain instead of relying on external contractors or suppliers. That is, the company owns or gains more control over two or more stages of its production or sales processes by bringing the processes in-house (through merger or acquisition).
A manufacturing company, for instance, integrates backward when it chooses to source its own raw materials instead of depending on a raw material supplier; and integrates forward when it chooses to sell directly to end customers, thus, eliminating its need for external distributors and retailers.
A typical example of a vertically integrated company, like Starbucks, for instance, integrates backward by owning its equipment, storage, and roasting facilities, as well as maintaining direct relationships with its coffee growers, thus controlling its entire manufacturing process. This coffeehouse company also integrates forward by owning its own retail shops and distribution centers for its product line of bottled and canned Starbucks coffee drinks.
Therefore, Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy is said to be a balanced integration strategy because the company uses both forward and backward vertical integration. Utilizing this strategy has been a huge part of this coffeehouse company’s corporate survival and success as it has helped it streamline its journey from raw materials sourcing to the delivery of its product to the end user. Thus, reducing costs and raising customer value.
See also: Telstra’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Does Starbucks use vertical integration strategy?

Starbucks uses a vertically integrated supply chain wherein the company is fully involved in every step of its supply chain. Unlike its major competitor, Starbucks controls every step of its supply chain; from plantation to production right through to the recyclable cup of coffee in a customer’s hand. That is, Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy involves ownership of all the supply chain assets and activities such as the coffee bean farms, coffee bean roasting plants, retail outlets, warehouses, and distribution assets.
The journey from a coffee bean plantation to a coffee cup involves a lot of processes and activities. Starbucks’ coffee supply chain involves growing, harvesting, hulling, drying, packing, blending, and roasting coffee beans. It also involves the complex web of transport and inventory management needed to accurately supply storefronts. Hence, Starbucks uses a vertical integration strategy to take charge of all these processes.
For instance, the company integrates backward by working directly with more than 400,000 coffee growers in 30 countries. These growers are trained on plantation techniques and quality assurance, which has enabled consistent production of beans to a greater standard of flavor and sustainability, thus, reducing Starbucks’ exposure to major supply disruptions.
The company also integrates forward by owning a handful of storage facilities across the globe to ensure that all coffee beans are roasted and packaged in the same way, which results in a coffee drink that tastes the same in every country. That is, Starbucks’ vertically integrated supply chain has no doubt made the company’s coffee and its customer experience better than those of its rivals.
Read also: Tesla’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Examples of Starbucks’ Vertical Integration Strategies
- The procurement process of Starbucks
- Starbucks’ transportation and warehousing strategy
- Retail outlets
- Mobile app and Currency Program
The Starbucks journey began in the year 1971 with a single store in Seattle; however, due to the vertical integration of Starbucks, the company has grown to become one of the most recognized brands across the globe. Starbucks is therefore one of the companies with vertical integration strategies.
Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy is focused on providing the best quality product while minimizing cost and environmental impacts. Hence, the company constantly innovates and invests in its supply chain in order to remain competitive. Here are examples of the various stages of the Starbucks value chain that are vertically integrated:
The procurement process of Starbucks
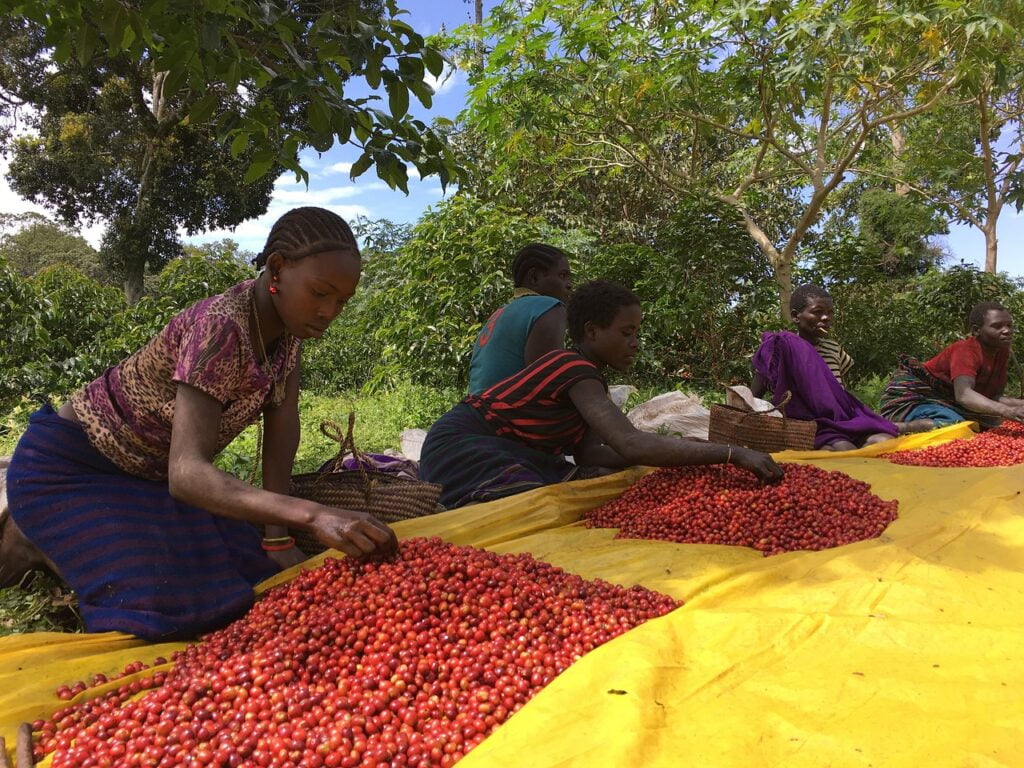

The procurement process of Starbucks is a typical example of a backward vertical integration strategy. A company integrates backward by either acquiring or merging with the subsidiaries that produce some of the inputs that it uses in the production of its products. The company can also integrate backward by establishing its own subsidiary to accomplish the task of its supplier like in the case of Starbucks.
Starbucks integrates backward by purchasing a 240-hectare coffee farm (Hacienda Alsacia) in 2013. This farm is located in Costa Rica and serves as a working farm for Starbucks as well as a global research and development facility. Nevertheless, the coffee bean farms that Starbucks owns are not enough to meet the full raw materials that the company needs and so Starbucks integrates solid purchase agreements with a wide range of coffee bean growers in order to ensure a sufficient supply of its raw materials.
Starbucks agents travel to Latin America, Africa, and Asia to procure high-grade coffee beans in order to serve the finest coffee drink to its customers. The green or unroasted beans are procured directly from the farms based on Starbucks established strategic relationship and partnership with the growers.
Starbucks is committed to only selling ethically sourced, Fair Trade coffee. Hence, it has its own Coffee Sourcing Guidelines (CSG) and Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E) standards that require all suppliers (coffee growers) to meet certain quality, ethical, and sustainability standards. Based on its standards, the company uses a stringent vetting process to ensure its growers meet and adhere to these guidelines.
The company, therefore, works directly with more than 400,000 coffee growers across the globe that conforms to its standards. Starbucks’ direct interaction with these growers ensures that all of its coffee beans achieve the same quality and flavor standards. It also makes the Starbucks supply chain less susceptible to major disruptions, like workers shortage or overplanting. Hence, this Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy gives it an edge over its competitors.
Starbucks’ transportation and warehousing strategy
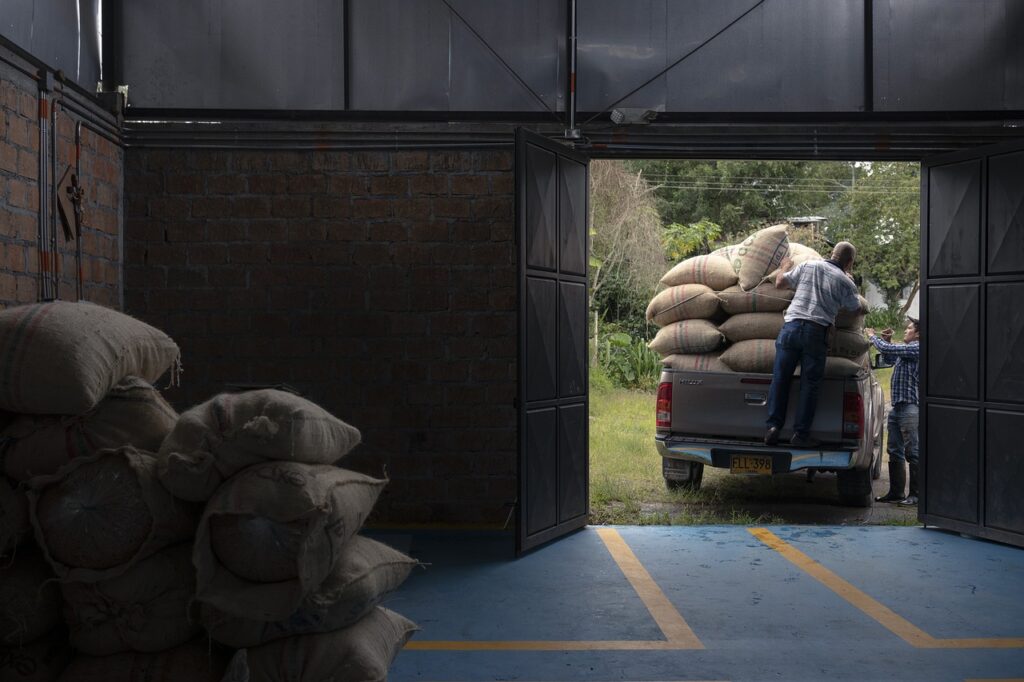

Starbucks’ transportation and warehousing strategy is an example of a forward vertical integration strategy. A company integrates forward by owning and controlling the business activities that are ahead in its supply chain such as the direct distribution or supply of finished products. Starbucks integrates forward by owning and controlling the direct distribution and supply of its products.
After the farmers pick and package the unroasted coffee beans, truckers take them to ocean liners that ship the beans to six storage sites in Europe and the U.S. In these storage facilities, the beans are roasted, packaged, and shipped to Starbucks’ distribution centers. Starbucks integrated forward by employing a regional distribution strategy wherein the company established four regional distribution centers, in order to streamline its transportation and warehousing operations.
Two of these regional distribution centers are established in the United States (one on the East Coast and one on the West Coast), one in Asia, and one in Europe. It is from these distribution centers that the company ships coffee and other products to its stores around the world. The company has a fleet of distribution trucks that deliver its products to stores and also has partnerships with a number of food and beverage distributors, who distribute Starbucks products to stores in their territories.
Retail stores are supplied by either smaller warehouses called central distribution centers (CDCs) or regional distribution centers depending on their location. Coffee and other items required by Starbucks’ retail outlets are held at these warehouses and regional distribution centers. The company uses 33 warehouses (CDCs) in the United States, five in Canada, three in Europe, and seven in the Asia/Pacific region; all these CDCs except one are controlled by third-party logistics companies.
These centers supply Starbucks’ own retail stores and retail outlets that sell Starbucks-branded products with coffee, tea, and other necessary supplies. Starbucks’ active participation in this stage of its supply chain (distribution) ensures that its distribution centers receive the products they need in order to fulfill orders and make their weekly deliveries on time. Therefore, this Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy has enabled Starbucks to improve its order fulfillment times and reduce its shipping costs.
One of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategies is establishing its factories, distribution centers, and warehouses in strategic locations in order to improve its performance in the marketplaces. For instance, Starbucks’ factories and warehouses located in Asia help to reduce transportation costs because some of the coffee beans are procured from this region.
Retail outlets

A company vertically integrates forward when it controls and owns the retail centers in which its products are sold. Starbucks uses forward integration by owning its own retail stores and working with large retailers such as Walmart and 7-11 convenience stores. This vertical integration of Starbucks makes it easier for coffee lovers to have access to Starbucks bottled coffee, capsules, and sachets while traveling or not at home.
Starbucks positions its retail stores as a place for connection and convenience for consumers. Consumers are usually happy when they can get what they want in a short amount of time. Hence, Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy of establishing its stores and partnering with third-party businesses and more physical stores at ideal locations enables the company to offer a greater reach to consumers.
Starbucks also owns pickup-only storefronts where customers pick up their orders in-store after ordering ahead on Starbucks mobile app. Starbucks’ first-ever pickup store was opened in November 2019. The company was early to the pickup-only game before the pandemic decimates dine-in traffic for restaurants and made pickup and delivery services a far more common concept for consumers.
By establishing pickup-only stores specifically for the mobile order occasion, Starbucks is able to control the delivery of its products for its customers using the store’s design, location, and the expertise of its baristas. This part of Starbucks’ vertically integrated supply chain has, therefore, made the company stand out among its competitors.
See also: McDonald’s Competitive Advantage
Mobile app and Currency Program
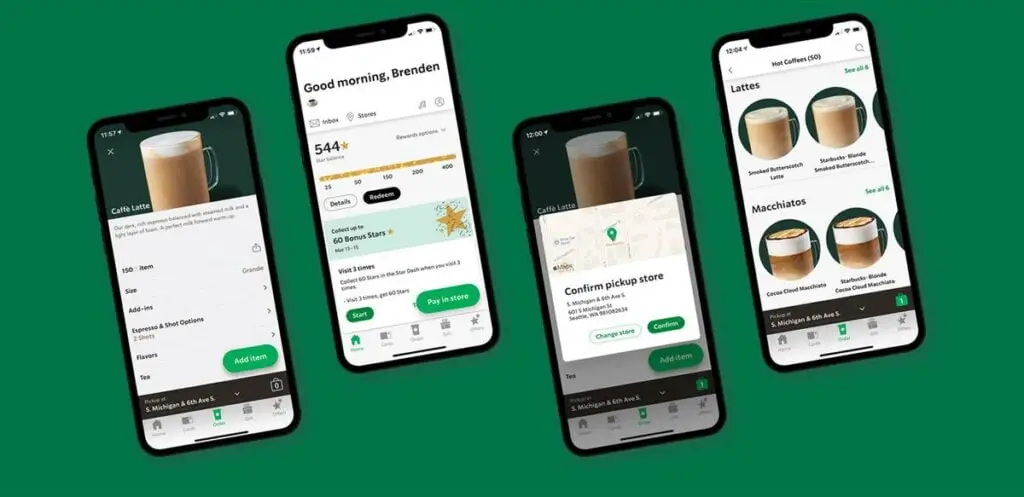
One of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategies is the introduction of its mobile app and currency program as another way of controlling the sale of its product to the public. Starbucks makes a move forward in the supply chain by using AI technology such as the Starbucks Mobile App to help make the ordering process more efficient and reduce service times which in turn improves the overall customer experience.
As technology is steadily being integrated into retail, Starbucks released its mobile app in 2009 and by 2014, customers could preorder on the app and make in-app payments. Starbucks’ mobile order & pay was a major breakthrough as it allows customers to pre-order food and drinks. Customers who order through the app from the comfort of their homes or workplace are able to avoid waiting in line (most of the time).
The introduction of Starbucks Mobile Order and Pay to its customers was to meet the needs of customization and convenience at any time of the day as pickup-only stores were established in various locations specifically for customers to pick up their orders.
The company also launched a currency program wherein customers receive digital stars for every Starbucks product purchased using the mobile app. With a single quick scan of the mobile app, customers can pay and earn rewards. This has incentivized customers to use the app for purchases more frequently, thus, the app accounts for more than 20% of all Starbucks sales.
Starbucks’ integration of the Mobile Order & Pay and currency program has helped the company to improve its customer relationships. This forward integration strategy increases personalization and improves Starbucks’ digital customer experience. Through the integration of the mobile app, personalization is increased as the app recommends drinks to customers based on their search histories and buying habits.
Furthermore, this Starbucks vertical integration strategy makes Starbucks closer to its end consumers and increases the company’s efficiency. Starbucks pioneering mobile app has also made the company stand out among quick-service restaurants (QSRs) as a digital leader. For example, during the pandemic, compared to its competitors, Starbucks was able to make sales and have more seamless transactions because mobile order & pay was definitely a contact-free option for contagion-conscious customers.
See also: Horizontal Integration Examples of Companies
Advantages of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy
- One of the advantages of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy is that, as the company has ownership of the entire supply chain, quality is guaranteed all the way through its supply chain.
- The backward vertical integration of Starbucks makes the company price-competitive because it is not reliant on the raw material market or at the mercy of the coffee growers’ pricing strategies.
- One of the advantages of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy is that it makes the Starbucks supply chain less susceptible to major disruptions which gives it an edge over its competitors.
- Starbucks’ vertically integrated supply chain gives it a competitive advantage over Dunkin’ Donuts, its biggest competitor in the international coffee market, which relies on a third-party intermediary to handle its supply chain operations; Starbucks started roughly twenty years after Dunkin’ Donuts but is already much larger than this company. Relying on third party suppliers has its benefits but also comes with some issues as can be seen in Nike’s Supply Chain Issues and Management.
- Unlike Dunkin’ Donuts which franchises nearly all of its retail stores, Starbucks franchises just less than 50% of its retail stores which allows the company to have more control over how its brand is presented to consumers and also consolidate the company’s operations.
- Another prominent advantage of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy is that the solid purchase agreements with coffee bean growers based on Starbucks C.A.F.E. practices and CSG helps the company to get the best quality coffee beans and other ingredients at the lowest cost.
- Due to Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy, the company is committed to using 100% sustainably grown, Fair Trade-certified coffee beans, compared to Dunkin’ Donuts which promises to produce its coffee as sustainably as possible but only offers two permanent menu items that are Fair Trade-certified.
- The vertical integration of Starbucks gives the company a larger global presence and increases the revenue it generates; in 2019, for instance, Starbucks earned about $26.52 billion U.S. dollars in revenue while Dunkin’ Donuts generated about $1.37 billion U.S. dollars.
- Another advantage of Starbuck’s vertical integration strategy is that it enables the company to primarily market to higher-income customers looking for a premium coffee experience, compared to its rival which has traditionally retailed to more blue-collar consumers.
- As a result of Starbuck vertical integration strategies, the company has a greater market share because customers are willing to pay more for the Starbucks coffee that they perceive to be made from higher-quality, socially responsible sources; customers also pay more to enjoy the amenities offered in the company’s coffeehouses.
- Starbucks’ supply chain strategy enables the company to minimize costs while ensuring their customers get the freshest coffee and other products; this is definitely one of the benefits of vertical integration.
- Vertical integration strategy by Starbucks also involves using technology (like the Mobile App) to streamline operations has enabled the company to get closer to its end consumers and increase its efficiency.
- All the implemented Starbucks vertical integration strategies have helped to reduce waste, increase sustainability throughout the Starbucks supply chain and give the company a robust supply chain that responds quickly to changes in customer demand.
Read also: Blockchain marketing strategy and Benefits
Disadvantages of Starbucks’ vertical integration strategy
The main reason companies adopt vertical integration in their business model is to increase production efficiency and reduce disruption in their supply chain. Nonetheless, vertical integration has its disadvantages; this strategy is not usually easy to pull off unless the company has more than enough resources to integrate forward or backward.
In as much as the successful vertical integration of Starbucks has benefitted the company, it has cost the company a lot of financial obligations. That is, one of the disadvantages of Starbucks’ vertical integration is the higher costs incurred and capital required while taking ownership of any of the stages in the value chain. Every step of the supply chain that Starbucks acquires is very expensive to start up because it requires billions of dollars to be spent on mergers or partnerships with other companies, infrastructure, logistics, technology, logistics, etc.
The higher costs incurred can affect the profitability of a business and put pressure on the business’s financial resources. This means that, if Starbucks’ vertical integration strategies are not carefully planned and failure occurs, the company will definitely experience a setback in its finances and may go bankrupt. For instance, Starbucks integrated forward by spending a huge amount of money to establish its retail pick-up stores debuted in late 2019. With such investment and an unexpected pandemic occurring the following year, Starbucks is expected to experience a serious setback in its finances.
However, in as much as Starbucks, just like other companies, experienced a decline in sales (an 11.28% decline in revenue from 2019) during the pandemic, the investment in pick-up stores was an advantage considering the social distancing and isolation protocols that were strictly adhered to, in 2020. Therefore, had this vertical integration investment not come in handy for Starbucks’ contagion-conscious customers, the investment would have caused an enormous strain on the company’s finances at the time.
Related:
- IKEA Supply Chain Problems and Issues
- McDonald’s Supply Chain Issues and Process
- Netflix’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
- Telstra’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Obotu has 2+years of professional experience in the business and finance sector. Her expertise lies in marketing, economics, finance, biology, and literature. She enjoys writing in these fields to educate and share her wealth of knowledge and experience.
