The value chain activity is comprised mainly of primary and secondary activities undertaken by business corporations when creating a product or service. These value chain activities generally progress from one stage to the other until the product or service created gets to the end-user or consumer.
Understanding the various processes that comprise a company’s value chain aids the company by providing invaluable insight into how effective and efficient its value chain activities are. It also provides clarity on the competitive advantages available to a company through the maximization of its value chain activities.
Before we discuss the primary and support value chain activities, let us define what a value chain means.
Read about: Value Chain of Starbucks: Examples and Analysis
What is a value chain?
A value chain refers to the progressive activities and processes required to create a valuable product or service for the consumer. This usually consists of several stages starting from the ideation of service creation or the sourcing of raw materials, through other stages such as research and development, processing, packaging, distribution, sales, and all other stages that lead to the final product.
The value chain is a business management concept that was propounded by Harvard Business School Professor, Michael Porter in his book, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance which was published in 1985.
When the value chain of a company is examined to determine how it functions especially with the aim of identifying and improving areas that are inefficient, the process is referred to as value chain analysis.
Read about: McDonald’s Competitive Advantage
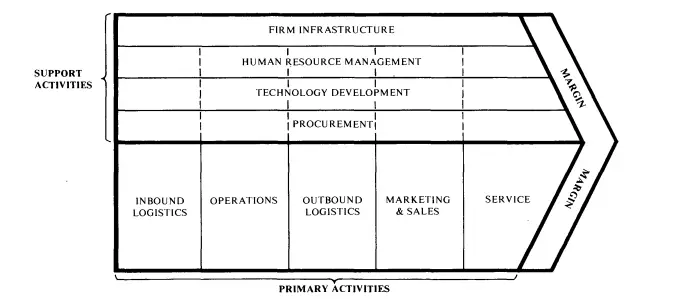
Value Chain Activities
- Primary activities
- Secondary activities
Listed above are the 2 value chain activities as identified by Michael Porter. No matter the industry, these activities are found in most business operations although certain aspects may be more pronounced in certain industries than in others.
Primary activities of the value chain
The primary activities of a firm refer to those activities that are directly concerned with the creation of a good or rendering of a service. These activities are broadly divided into:
Inbound logistics
This is the first activity in the primary value chain. It refers to all activities associated with receiving, storing, and disseminating raw materials and components needed for the production of a good. These raw materials and components usually come from suppliers to the factory or assembly plants.
Inbound logistics generally includes material handling, warehousing, inventory control, vehicle scheduling, and returns to suppliers.
Operations
This aspect of the value chain is concerned with the conversion or processing of raw materials into finished goods or the assembling of parts and components into a product.
Operations include machining, packaging, equipment maintenance, assembling, testing, printing, and facility operations.
Outbound logistics
This aspect of the value chain activity deals with the collecting, storing, and distribution of the finished product from where it has been manufactured to distribution centers, depots, stores, or warehouses where consumers can get it.
The activities in outbound logistics include finished goods warehousing, material handling, delivery vehicle operation, order processing, and scheduling.
Marketing and sales
Marketing and sales deals with all the strategies employed by a company to inform people about its products, encourage them to enquire about the products, provide them with a purchasing channel, and induce them to make a purchase.
The activities in this step of the value chain include marketing, promotion, sales force, quoting, channel selection, channel relation, and pricing strategy.
Service
Service is the last stage in the primary value chain activity. It includes all activities that occur after a consumer has already purchased the product or service. These activities are aimed at enhancing or maintaining the value of what has been bought.
Service activities include installation, training, repair, parts supply, product adjustment, and customer service.
Secondary activities of the value chain
- Procurement
- Technological development
- Human resources management
- Infrastructure
All secondary activities of the value chain are closely related and make the primary activities more efficient. They, in turn, aid companies in maximizing their competitive advantages. Secondary activities are also referred to as support activities.
Procurement
Procurement includes all activities related to the purchase of raw materials, parts, equipment, and all physical assets needed in the production of a good or provision of service.
Common activities under procurement include seeking suppliers, maintaining supplier relationships, and negotiating prices.
Technological development
No company can continue thriving without adequate technological development. This can vary from the technology needed in optimizing various processes within the organization to those directly needed in the creation of a good or service.
Some value chain activities found under technological development include market research, product design, and process automation.
Human resources management
Human resource management is the bane of every business as personnel are needed for the effective functioning of the different aspects of the firm. Through human resource management decisions and activities relating to finding new talents, hiring, training, staff development, retention, and compensation of employees are taken care of.
Infrastructure
This supporting value chain activity is concerned with a company’s organizational framework. It deals with how the company operates, determines how activities are carried out, and ultimately lays out the chain of command as well as how each department relates with the other.
Infrastructural activities include management, quality assurance, overhead, financing, and public relations.
Read about: Lululemon’s Competitive Advantages and Strategy
What are the 5 primary activities of a value chain?
The five primary activities of the value chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and services.
Read about: Tesla’s Competitive Advantage and Strategy
Value chain activity examples
In order to understand how the value chain practically functions, we shall use the tech giant, Apple as an example. We shall trace the various value chain activities that occur within this company using the primary and supporting value chain activities.
Read about: Costco’s Competitive Advantages and Strategy
Examples of the primary value chain activities of Apple
Inbound logistics
The inbound logistics of Apple involve the company’s sourcing and purchase of the various parts and components that are needed for its phones and laptops.
The brand has a vast network of suppliers scattered across China, America, and Europe which it relies on to supply it with software and hardware for its products. Some of the brand suppliers include 3M and Foxconn. The former supplies Apple with touch films while the latter manufactures the iPhones.
Apart from suppliers, Apple has employed vertical integration by producing some of its software such as the chips used in its iPads and iPhones in-house.
The brand also owns the operating system used in its gadgets. This way, the brand curtails its dependence on external suppliers for software.
Example of operations
In the aspect of operations, Apple has 5 reportable operating segments which include greater China, Americas, Europe, Japan, and the rest of Asia Pacific. Among these 5 regions, China accounts for about 95% of product manufacturing and assembling due to the availability of cheaper components, and labor amongst other considerations.
Example of outbound logistics
Based on Apple’s position as one of the biggest tech companies in the world, the brand’s outbound logistics comprises a robust distribution network that gets its products to consumers. Through the company’s physical and online stores, customers can buy the brand’s products either in-store or online.
The brand has also partnered with several retailers through whom its teeming customers can access the brand’s products. One such partnership is with the retailer, Target.
Through these direct and indirect distribution channels, consumers can easily purchase any Apple product they want such as iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, AirPods, HomePod, Apple TV, and other Apple accessories.
Marketing and sales
Despite being a well-known brand, Apple still markets its products to increase and encourage patronage. Its marketing efforts include traditional advertising such as television and print as well as digital marketing such as the use of internet commercials, website ads, and social media.
When it comes to sales, the company’s products can be bought directly from the company from its direct sales forces, physical or online stores. Consumers can also make a purchase for wholesalers, retailers, value-added resellers, or third-party cellular network carriers.
Services
Apple provides top-notch services to its consumers through different stages. Before purchase, individuals can window shop at Apple stores to better understand the features and capabilities of the device they want to buy.
After making a purchase, customers enjoy up to one year warranty on the product and if eligible, they could get free repairs within the warranty period. Additionally, the brand has an upgrade program through which individuals can update their gadgets to a more current version at an additional cost.
For Instance, individuals who own the iPhone 14 could trade it in for the iPhone 15 provided that they met the requirements outlined by the brand.
All these services are hinged upon the effective and efficient team of tech-savvy employees that the brand uses in its stores worldwide.
Examples of the supporting value chain activities of Apple
Procurement
Apple has a procurement department that oversees the various purchases made by the company for the different components needed for its gadgets. This department ensures a smooth relationship between the company and its suppliers.
Additionally, due to the large scale of purchases made by the brand, most of its suppliers ensure that they maintain the good business relationship they have so as to continue being patronized by Apple. This has also been helpful in giving the company access to the needed quality components.
Technological development
The technological development of Apple can be seen in the evolution of its product designs with every new model it makes. The brand reportedly spent $26.251 million on research and development in the fiscal year ended 2022.
The brand’s consistent commitment to research and development is geared towards providing better products to its consumers and continuously expanding and maintaining its competitive advantage in the market as the provider of premium quality gadgets.
Human resources management
Apple’s human resource department oversees the company’s recruitment and hiring of new employees. They also take care of all employee-related issues ranging from complaints to compensation and leave.
Right from the brand’s inception, the brand has been known for providing its employees with a competitive compensation package. The company is also committed to current employment trends geared at having a workforce that supports diversity and inclusion.
Infrastructure
Being a multinational company. Apple has a clear-cut infrastructure that outlines the chain of command in the organization. It also has several departments that handle different aspects of the organization. However, the vertical structure of the company ensures that everything is ultimately overseen by the CEO who is at the helm of affairs.
Conclusion
The primary and supporting value chain activities are a significant part of every organization. This is because these activities determine how an organization functions and also enhance its competitive advantage.
Last Updated on November 2, 2023 by Nansel Nanzip BongdapBlessing's experience lies in business, finance, literature, and marketing. She enjoys writing or editing in these fields, reflecting her experiences and expertise in all the content that she writes.
