Nestlé’s supply chain comprises a network of suppliers, mainly in the food and drink industry. It also consists of contractors in the cosmetic and consumer healthcare industry. Thus, the company has to implement specific supply chain management strategies to curtail any issues that may arise due to working with such a broad network of suppliers.
Nestlé was created in 1905 through the merging of two companies, the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company and Farine Lactée Henri Nestlé. The former was established in 1866 by brothers George and Charles Page while the latter was founded by Henri Nestlé in 1867.
After the merger of these two companies, the new company was referred to as the Nestlé and Anglo-Swiss Condensed Milk Company. When the company acquired Alimentana SA in 1947, the brand name was changed to Nestlé Alimentana SA. By 1977, the company’s name was shortened to Nestlé S.A. which is being used by the company until now.
Another significant acquisition by Nestlé was the acquisition of Ergon in 1916. Ergon had patented a spray drying process that enabled the production of milk powder. The acquisition of Peter-Cailler-Kohler in 1929 enabled Nestlé to participate in the production of chocolate; which grew to become a huge part of the business’ products.
As of 2023, Nestlé operates over 340 factories in 77 countries. Its teeming workforce comprises around 275,000 employees and its products are sold in 188 countries across the globe.
The company comprises over two thousand (2,000) brands that produce goods ranging from baby foods, coffee, breakfast cereals, soups and sauces, pet food, bottled water, chocolates, seasoning, ice cream, milkshakes, etc.
Based on business valuation by Forbes which took into account the market value, revenue, assets, and profit of companies, Nestlé ranked as the world’s largest food and beverage company in 2023.
Here, we shall discuss Nestlé’s supply chain strategy, focusing on how the company is able to effectively manage its supply chain and some issues that arise in the process.
See also: IKEA Supply Chain Problems and Issues
What is a supply chain?
Supply chain refers to the network of individuals and corporate organizations that are involved in all the processes undergone to convert raw materials to finished goods.
A supply chain generally begins with the production and sourcing of raw materials to its distribution to processing plants and product manufacturers and ends with the final delivery of the product to consumers.

See also: Starbucks Supply Chain Issues and Management
What is the supply chain of Nestlé?
The supply chain of Nestle comprises a network of farmers, suppliers, and contractors who are responsible for the production and aggregation of the various ingredients that the company requires for the production of the numerous items it manufactures. It also comprises firms, companies, and retailers who are involved in the transportation, distribution, and sale of products to consumers.
This means that Nestle is somewhat in the middle of the supply chain. The beginning of the supply chain comprises mainly raw material producers and logistics partners while the ending consists of product distributors and retailers.
At each stage of Nestle’s supply chain, there exists a significant number of individuals and companies that work closely with the brand to ensure that raw materials get to the company, are processed into valuable items, and get distributed to the end users (consumers).
Nestle’s commitment to food safety and its adherence to quality standards ensures that consumers can access diverse food and beverage options of high quality made with utmost consideration for the sustainable use of resources.
See also: McDonald’s Supply Chain Issues and Process
Nestlé supply chain process
- Sourcing of raw materials and suppliers
- Manufacturing of products
- Warehousing and distribution to retailers
- Retail stores and online markets
Throughout Nestle’s supply chain process, supply chain teams play a vital role. They work with farmers and suppliers to ensure that raw materials are sourced responsibly, on time, and in the right quantities to meet manufacturing requirements.
They also work with the manufacturing department to plan production quantities to balance inventory levels so as to meet the desired number of products to meet market demands.
Nestle supply chain teams are also responsible for the sustainable and safe storage of all manufactured products. They also oversee product delivery to consumers and customers through the vast network of logistics partners and retailers.
Sourcing of raw materials and suppliers
The first step in Nestle’s supply chain process is the sourcing of raw materials; this is done by the company’s procurement team.
Nestle purchases the raw materials needed for their products directly from the farmers or through product aggregators and farmer cooperatives. As of July 2022, it was reported that Nestlé works with over four million farmers and consumes about 1% of the world’s agricultural output.
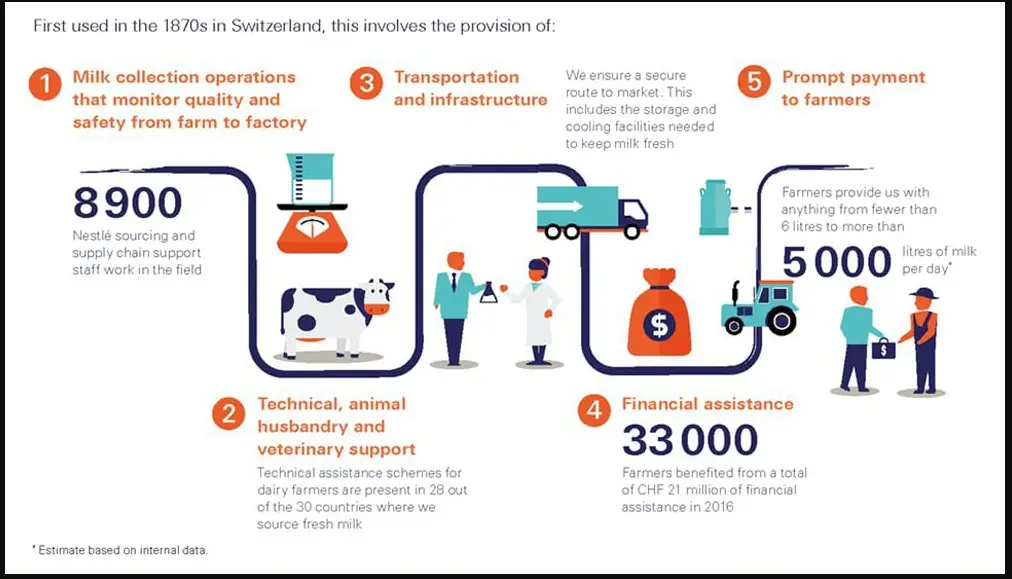
The major ingredients the brand purchase include cereals and grains, cocoa, coffee, coconut, dairy, eggs, and hazelnuts. They also use fish and seafood, meat, palm oil, pulp and paper, spices, soya, sugar, and vegetables.
Nestle’s procurement team obtains these raw materials in a commercial way to certify providing quality, avoiding delays in the acquisition of resources, and reducing the stock-out.
Nestlé suppliers list
| Name of Nestle supplier | Raw material supplied |
|---|---|
| ADM Corn Sweeteners | Corn and wheat |
| Barry Callebaut | Cocoa |
| Aspinwall & Co.IN | Coffee |
| Carbery Food Ingredients | Dairy ingredients |
| OLAM International Ltd | Hazelnuts |
| Misamis Oriental | Coconut |
| Bunge Loders Croklaan | Palm oil |
| Tyson Foods Inc | Meat |
| Sucrivoire | Sugar |
| Worlée NaturProdukte GmbH | Vegetables |
| Mountain State Oilseeds | Mustard seed |
| Bohemilk, A.S | Dairy ingredients |
| Solteam | Soya |
| Paras Spices | Chili, Cumin, Coriander, Turmeric |
| Winstone Pulp | Paper |
| Pacific Sugar Corporation Limited | Sugar |
| Weidemark Fleischwaren GmbH | Meat |
| Dairy Farmers of America | Dairy ingredients |
| Luchinger + Schmid AG | Eggs |
| 3D Corporate Solutions | Poultry |
| Beijing Findik Foods Co., Ltd | Hazelnuts |
| Alagoas | Coconut |
| Cargill | Corn, cocoa, palm oil, soya, and wheat |
| Gemini Edibles & Fats | Palm oil |
| Morning Star Packing Co | Vegetables |
Manufacturing of products
The manufacturing of Nestle products is carried out in different factories that are involved in the production of the company’s numerous products under its over 2,000 brands.
For instance, Nestle produces a cereal made from maize and soya for its West African market in Nigeria. This cereal is referred to as Golden Morn in Nigeria and Cerevita in Ghana. The production of confectionaries such as Milky Bar, Aero, and Kit Kat is done at Nestle’s York factory in the United Kingdom.
The diversity in manufacturing locations for different products ensures that the company gains easier access to raw materials and maintains the quality of production to meet nutritional and other standard requirements.
The products manufactured by Nestle brands are classified under confectionery, powdered and liquid beverages, milk products and ice cream, water, nutrition and health science, petcare, and prepared dishes and cooking aids.
Warehousing and distribution to retailers
Similar to product manufacturing, the warehousing and logistics aspect of Nestle’s supply chain process is equally handled by a network of different companies. This is due to the diverse manufacturing outfits the brand uses and the different countries where its products are purchased.
Although Nestle carries out some of its warehousing and logistics in-house, it also partners with warehousing and logistics companies across the globe including XPO Logistics, DHL, Fabeto Nigeria Limited, and Kuehne + Nagel.
These partners handle different products in different parts of the world. For instance, the partnership with DHL covers the warehousing and distribution of Coffee Mate, MILO, and Nescafé in parts of Asia Pacific such as India, Burma, Malaysia, Vietnam, Australia, Thailand, New Zealand, and Taiwan.
Retail stores and online markets
Nestle’s supply chain process ends at retail stores and online platforms where individuals can easily access the company’s products. Some of the most common retailers that sell Nestle products include Walmart and Target.
The products can also be gotten at other regional and country supermarkets and grocery stores as well as some local stores within communities.
See also: Nike’s Supply Chain Issues and Management
Nestlé supply chain diagrams
- Cocoa supply chain diagram
- Pulp and paper supply chain diagram
- Palm oil supply chain diagram
Cocoa supply chain diagram
Nestle collaborates with farmers and diverse suppliers for its cocoa supply. Cocoa is a key ingredient in the brand’s confectionery products, especially chocolate.
Pulp and paper
Pulp and paper are significant items in Nestle’s supply chain. It is used for making various product packaging as well as for correspondence within the organization. Below is a typical pulp and paper supply chain for the brand.
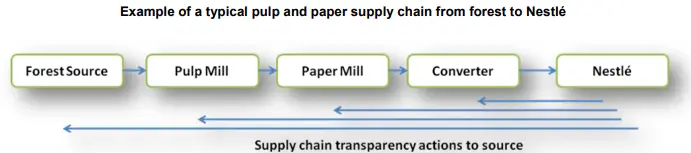
Source: Nestle
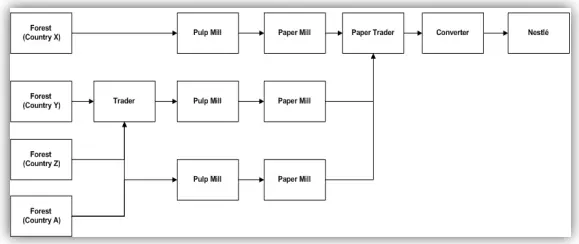
Most times, the supply chain may be a little more complex; involving a combination of forest workers, traders, pulp and paper mills as well as converters. In such a scenario, the supply chain diagram will be as shown below:
Palm oil supply chain diagram
Nestle uses palm oil as an alternative to sunflower oil in some of its products such as the Uncle Tobys Roll-ups.
See also: Subway Positioning and Marketing Strategies
Nestlé supply chain management
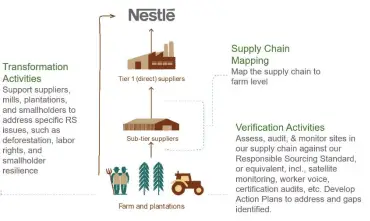
Nestle’s supply chain management is handled by its procurement and supply chain team of employees. These collaborate with other departments within the organization as well as farmers, suppliers, and other partners within the supply chain.
The brand has established several projects and initiatives that enable them to have as much direct contact as possible with the farmers of the ingredients they use. These initiatives are geared toward better managing the supply chain. It is also aimed at improving the quality of ingredients as well as the lives of the farmers.
In the united states, for example, Nestle has worked with pumpkin farmers in central Illinois to implement regenerative practices in more than seventy fields that comprise about 6,000 acres. These have aided in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 732 tonnes and also lowered soil erosion rates by 40%.
Nestle has also gotten directly involved in dairy production through the establishment of some net zero dairy farms across the United States, Switzerland, Pakistan, and South Africa. These farms have significantly reduced the number of cows kept while improving milk yield. Hence, serves as an effective supply chain management practice.
The company’s procurement team works together with its commercial teams and suppliers to develop forecast demand. This guides the quantity of raw materials that the company purchases from suppliers.
The establishment of procurement hubs in Switzerland, Panama, and Malaysia aid in Nestle’s supply chain management by making it easier for the company to aggregate the various raw materials it uses as well as enable easier distribution to its factories.
The procurement hubs are well distributed to ensure that supply chain issues such as the short supply of raw materials are effectively tackled and production quarters effectively met.
Nestle’s commitment to sustainable use of resources and waste management as well as its transparency in disclosing the suppliers in its supply chain further add to the smooth functioning of its supply chain.
The brand’s use of cutting-edge technology for its operational planning including demand sensing and production scheduling has helped Nestle to improve the flexibility and stability of its operations. The company reports that its use of technology in its supply chain management has enabled the brand to respond to consumer demand rapidly and effectively.
See also: Disney’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Nestlé supply chain issues
- War-time challenges
- Nestle supply chain shortages
- Nestles supply chain issue of forced and child labor
- Sustainability issues
Similar to other companies, the Nestlé supply chain also has some issues which it has faced in its over one hundred years of existence. Some of these Nestlé supply chain issues have been listed above and will be discussed in detail below:
War-time challenges
- Surge in demand
- Decrease in demand
- Ingredient shortage
Surge in demand
Nestlé supply chain issue due to war first occurred in 1914 when war broke out in Europe that subsequently extended to world war 1 and later in 1939 when world war 2 broke out. The wars led to shortages in raw materials, particularly milk, due to the slowing down of cross-border trade and hostilities between countries.
The milk shortage in Switzerland where the company’s factory was situated also meant that the company had to forgo the production of condensed milk for export in order to meet local demands. Thus, the brand gave its fresh milk supplies to assist the people that lived in the country.
Although these were challenging times for the company, it was also a time of higher demand for condensed milk and chocolate as various governments awarded contracts to the company.
In 1915 for example, the British Army included Nestlé’s condensed canned milk in the emergency rations given to its soldiers. This was informed by the ease of transportation and long-lasting nature of condensed milk compared to the more popular fresh milk of that time.
In order to meet demand and overcome the milk shortage, Nestlé brokered agreements with Australian companies to augment milk supply. The brand also acquired processing facilities in the United States to better meet the need of consumers within that region.
By the end of the wars, Nestlé had been able to adequately navigate the shortage and had grown its brand to include over 40 factories.
Decrease in demand
The decrease in demand after the war posed another supply chain issue for Nestlé. As government contracts ended with the war, the brand had surplus inventory due to its increased suppliers and factories.
The wall street crash further made the prices of goods plummet. It also reduced the purchasing power of individuals and households. These combined factors made the company experience its first and only financial loss since it began operations in 1905.
The brand soon overcame the issue as it was able to harmonize all its research through one laboratory in Vevey, Switzerland, and also appointed professional managers to oversee the company’s supply chain management.
Ingredient shortage
The global shortage of sunflower oil that started in 2022 is one of the issues that has affected Nestle’s supply chain. Sunflower oil has been used by the brand in some of its products such as Nestlé Milo cereals, Uncle Tobys Breakfast Bakes, Uncle Tobys Cheerios, Uncle Tobys Goodness Bowl Tasty Flakes – Honey and Almonds, Uncle Tobys muesli bars, and Uncle Tobys Roll-ups.
Due to the sunflower oil shortage, the company had to substitute this ingredient with canola oil or Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO segregated palm oil to ensure that production of the products earlier listed above was not halted.
Nestle however assured consumers that the change in the oil used did not change the texture, taste, or appearance of the products. It added that there might be a slight change in the nutritional profile of the items.
Nestle supply chain shortages
- Pandemic and yuletide shortage
- Shortages due to climate change and natural disasters
- Infant formula shortage
Pandemic and yuletide shortage
Nestlé’s supply chain issue of shortages that occurred due to the recent pandemic and surging demands during festivities is another challenge. The pandemic led to the global closure of borders and restriction of movements.
This meant that Nestlé’s supply chain particularly supplies, manufacturing, and logistics also got affected. The resultant effect was a decline in the company’s annual revenue from CHF 92.568 million in 2019 to CHF 84.343 million in 2020.
In the United Kingdom, a combination of the spillover effects of the pandemic and Britain’s formal exit from the European trading bloc in 2021 posed challenges for Nestle’s supply chain.
These caused challenges in the shipping of products and a significant shortage of Heavy Goods Vehicle (HGV) drivers. The resultant effect was an inadequate supply of the company’s confectionary products such as Lion bars, Kitkat, and Quality Street towards Christmas of 2021.
Despite Nestle facing these supply chain issues due to the pandemic and surging demands at festivities, the company’s chief executive in a statement to BBC assured consumers that despite the challenges, the company was working hard to ensure that it solves the shortages and meets consumer’s demands.

Shortages due to climate change and natural disasters
One aspect of Nestle’s supply chain that has been affected by natural disasters and climate change is its bottled water production. In California for example, the crippling occurrence of wildfires and droughts are posing a challenge to the company’s continued access to water from San Bernardino forest. Nestle bottles this water under its brand, Arrowhead Water.
In recent times, however, local environmentalists in the area have accused the brand of draining water supplies for profit at the expense of local communities and ecosystems. The environmentalist has also taken the company to court in a bid to stop them from utilizing the water.
Although the case is still ongoing, Nestle had refuted the environmentalists’ claims and insisted that the company had the right to utilize the water since 1865.
Although the brand sold this bottled water company along with some others in 2021, Nestle had other similar water supply chain issues in other parts of the United States including Michigan, Oregon, Maine, and Pennsylvania.
Infant formula shortage
In May 2022, there was a shortage of infant formula in stores across the United States. This left a lot of parents panicking about options for their kids; especially parents whose babies were intolerant of cow’s milk protein.
To tackle the shortage of infant formula, Nestle promptly began airlifting Alfamino milk and Gerber Good Start Extensive HA milk from its production plants in Switzerland and Netherlands into the United States.
The move proved helpful as it caused a gradual but consistent reduction in the shortages until it got tackled. The company also gained an additional 5% market share within this period due to its effective handling of the infant formula shortage.
Nestle’s supply chain issue of forced and child labor
Nestle’s supply chain has been reported of including forced and child labor in some of its processes. In 2015, it was reported that some individuals in the company’s fish supply chain were forced into working on the fishing boats.
In February 2021, the brand was also named alongside other chocolate manufacturers in a class action lawsuit for using child labor within their cocoa production supply chain. The case was however dismissed in June 2021 due to inadequate evidence.
The use of forced or child labor has been often employed by some producers as a means of accessing cheap labor. This is made possible due to a combination of several factors including lack of education, poverty, and local culture.
Nestle has however proven that they are adequately prepared and willing to handle such supply chain issues in ways that bring aid to the victims. In the case of forced labor in fishing, the brand has partnered with the sector’s industry association, the Seafood Taskforce, Royal Thai Government, and its suppliers to champion responsible recruitment of workers, improved conditions on fishing vessels, and provision of grievance reporting mechanisms.
In the case of child labor, the company has the Child Labor Monitoring and Remediation System (CLMRS). The systems aid the company in identifying children at risk of child labor, raising awareness, and providing remediation.
These steps have indicated that Nestle is effectively tackling its supply chain issues that may arise due to forced or child labor.
Sustainability and conservation issues
Nestle’s supply chain issue also includes sustainability. The growing concern of individuals, corporate organizations, and governments about the sustainable use of resources and protecting the environment has caused a lot of changes in the supply chain of Nestle.
This is because without sustainably using resources, we will be creating problems for future generations, especially regarding the emission of greenhouse gases which can deplete the ozone layer and exacerbate global warming.
In the bid to reduce the level of greenhouse gas emission associated with its supply chain, Nestle has been actively involved in taking various proactive steps to achieve this goal.
For instance, Nestle has introduced plant-based alternatives to its previously dairy-based products such as chocolate and milk. It has also formulated a new feed for cattle that produces less methane per liter of milk produced.
The brand has also invested about $2 billion towards developing alternative packaging for its products that can reduce the company’s use of virgin plastics by one-third in 2025.
Nestle is further tackling issues of sustainability and resource conservation by using a shared distribution with other companies to avoid having empty trucks after the delivery of products to retail centers. The brand has also converted about 75% of its trucks from diesel to Bio-LNG.
Nestlé experts are working to identify the most suitable pulses and grains for low-carbon, plant-based alternatives to meat, seafood, and dairy.
Another way the brand is pursuing its sustainability goals is through the establishment of the Nestlé Institute of Agricultural Sciences. The brand aims to translate and implement the various novel agricultural ideas developed by the institute into concrete and applicable projects so as to further regenerative farming and reduce carbon emissions.
The brand has also been working to achieve deforestation-free primary supply chains for its forest-risk raw materials such as sugar, meat, pulp and paper, palm oil, and soya by the end of 2022. It also aims to achieve the same for coffee and cocoa by 2025.

Nestle has also targeted growing over 200 million trees and investing in about 15 landscape initiatives by 2023. All these moves and changes are some of the ways Nestlé is tackling this supply chain issue of sustainability.
See also: Netflix’s Vertical Integration Strategy and Examples
Conclusion
Nestlé’s supply chain is robust and the brand has been committed to improving its supply chain through the adoption of various initiatives. Some of these initiatives involve educating farmers on best farming practices to improve yield, aiding livestock and poultry growers to achieve free-range grooming of animals, and using technology to ease tracking of inventory as well as supplies to retailers.
Although Nestle has faced various supply chain issues ranging from lawsuits to raw material shortages, the brand has shown its efficiency, flexibility, and adaptability by quickly managing the problems and ensuring quick resolution.
See also: Tesla Competitive Advantage and Strategy
Last Updated on November 2, 2023 by Nansel Nanzip BongdapBlessing's experience lies in business, finance, literature, and marketing. She enjoys writing or editing in these fields, reflecting her experiences and expertise in all the content that she writes.

